Table of Сontents
Introduction
The valuation of the computer vision (CV) global market stood at $14.9 billion in 2022. Interestingly, a report highlights that this market will cross $20 billion by 2030. The fact is that computer vision applications continue to get more mainstream.
When automating repetitive human tasks and maintaining high accuracy, it has become clear that thus technology has become advanced enough to cover a lot of areas in different industries and maintain its momentum for years to come. Continuous advancement and adoption of computer vision applications depend on how fast AI models evolve.
A survey shows that CV has been expanding at lightning speed. AI technology is moving faster than business leaders and trendsetters can keep up with it. Still, most companies across different industries now want to invest heavily in AI-powered solutions.
So, what are we talking about it today? Current industry challenges, computer vision tasks, and its advantages. Let’s touch on how different industries are utilizing this technology with real-world examples:
How Different Industries Utilize Computer Vision
Retail

The retail sector has always been eager to test innovations. AI solutions in retail help to better understand customers, analyze their emotions during purchases, create personalized promotions, forecast demand and sales, calculate conversion rates, and much more.
Let’s explore a few examples.

1. Analysis of Shelf Placement
Computer vision assists in analyzing the arrangement and availability of products on store shelves. This optimization enables better product placement to enhance sales.
Example: Several major retailers and manufacturers utilize solutions for shelf analysis. For instance, a tobacco product manufacturer employs the Goods Checker application. It compares shelf photographs with planograms, identifies incorrectly placed or missing items, generates detailed analytical reports for managers, and helps assess shelf performance. It also determines the brand’s shelf share and that of competitors.
This solution provides real-time insights into shelf conditions, enhances store auditing speed and accuracy, and aids in logistic planning and timely product delivery.

2. Customer Behavior Analysis
With AI algorithms, it has become possible for retailers to extract solid insights about their customers’ behaviors in real time. This is a far more efficient approach to learn about changing customer behaviors and preferences rather than use traditional observation methods.
It involves analyzing customer emotions and movements toward products. What’s exciting is that FMCG companies can personalize their tactics to make people’s shopping experience more seamless and engaging.
Let’s dive into a few examples.
Examples: From supermarkets like Walmart to prestigious brands like Louis Vuitton, it has become common to utilize CV to keep an eye on in-store customer movements. The idea is to use this technology to pinpoint the most sought-after products and sections. It allows retailers to improve their promotional displays and store layouts.
But that’s not all – it allows retailers to deduce customer sentiment. As a result, it makes it possible for retailers to measure the performance results of a marketing campaign and merchandise placement.
So, suppose a customer often interacts and stops around a specific product display or section. In that case, retail can take proactive action and improve the promotional designs and offers around that specific product line. In another example, consider an electronics retail store that utilizes computer vision to review on-site customer behavior.
Now, electronics retailers can spot “when” and “why” customers are having difficulty finding a specific product or need answers to some questions. And that’s because it’ll allow that electronics store to analyze facial expressions and monitor customer movements in-store.
With computer vision in place, retailers can count on dedicated and automated alerts that sales professionals can use to offer prompt assistance and support to those customers. It’s a win-win for the electronics retailer – it can boost sales and improve shopping experience at the same time.

3. Automated Checkouts
Every time you see an automated checkout – know that it likely works around computer vision. In fact, automated checks are one of the hallmark elements you associate with modern-day retailers and continue to make them popular. Automated checkout systems minimize waiting periods, improve customer satisfaction, and speed up the shopping process.
Let’s check out a couple of examples.
Examples: You’ve probably been to your local grocery store and have noticed that they use kiosks and automated checks that support object detection. It allows shoppers to just put their items in the scanning area. After that, the kiosk system utilizes AI so that it can identify and tally all the items. Automated checkouts cut out the need to depend on a cashier to calculate items. As a result, it makes the shopping experience more compact and efficient for people.
Take major store departments, for example. They also use computer vision and support mobile apps so shoppers can self-checkout from their smartphones. Shoppers just need an app to automatically calculate the cost of items they want to scan and then complete the shopping process. Shoppers can also pay via the app and avoid having to deal with long checkout lines.
Automated checkouts work in favor of shoppers and staff – it saves both of their time. For store staff, it is more important and allows them to focus on more important tasks involving customer service.

4. Staff Work Schedule Visualization
Without proper staff scheduling and planning, retail operations will fall apart. CV helps store managers visualize and improve employee schedules. How does computer vision work? It uses store traffic in real time and allows retailers to ensure that their resource allocation is efficient 24/7.
Let’s look at two essential examples:
Example: Major retail chains now utilize this technology to track customer foot traffic every day. The idea to review such data is to not just have compatible staff schedules – it helps managers ensure a specific number of employees should be present on the floor. Retail traffic does not always hit peak hours, which is a great way to cut back on labor costs amidst slow traffic periods.
Many retailers now use AI-automated attendance. What’s appealing is that these systems come with added features that allow retailers to be on top of time tracking and management. It allows retail managers to move away from manual time tracking and alleviate the usual administrative burden.
Computer vision tech helps retailers track staff levels in real time. When running in-store operations, managers know that most operational elements complement each other. This technology allows retail managers to assign resources to meet specific customer demands.
Time and time again, retailers with efficient employee scheduling are more likely to offer high-quality customer service, reduce labor costs, optimize operations, and boost sales.

5. Preventing Theft
Theft has always been one of the major issues in the retail sector. Fortunately, retail prevention has come a long way, and computer vision couldn’t be a perfect tool for retailers to improve their in-store security. Smart video analytics are at the forefront of curbing and preventing retail theft.
Here are two best examples:
Examples: Companies can now pair smart video analytics with CCTV cameras. It makes it possible for retailers to improve their network security. Essentially, these systems are powered by AI algorithms and can analyze real-time live feeds. In fact, more and more retailers now count on these systems to spot suspicious activities like product tampering, weird customer behavior, and shoplifting.
On the other hand, big department stores use intelligent video analytics to track in-store activities on a much larger scale. But the system functions are the same: detect behaviors like loitering and concealing items. It automatically disseminates alerts and notifications to the department store’s security team.
After that, security personnel can analyze the footage and involve law enforcement agencies if someone is found loitering or stealing items. Theft prevention also works through facial recognition.
Many retailers now use dedicated AI-powered facial recognition solutions and pair them with their security systems to backtrack the history of suspicious behavior of shoplifters. Today, top-of-the-line boutiques use facial recognition systems at the front of their stores.
So, as soon as an individual goes through the entrance, the facial recognition cameras analyze facial features and track suspicious activity. And if someone with a loitering or shoplifting background enters the store, the facial recognition system alerts the manager.
Manufacturing

The modern-day manufacturing sector continues to adopt diverse automation solutions, and computer vision remains at the center. After all, it helps manufacturers minimize safety risks, improve production efficiency, and automate quality control.
Industry 4.0 represents a new manufacturing paradigm where the industry wants to embrace automation solutions and set new standards. The manufacturing industry uses a combination of robotic technology, IoT devices, deep learning algorithms, and AI models in tandem.
CV has become a major tech to help manufacturers transform different elements of their production through smart automation solutions. Once manufacturers implement this technology, they can automate quality control, speed up production, raise quality standards, minimize operational errors, and much more.
Manufacturers can also implement tracking systems to minimize inspection time, help operators be more efficient, and reduce on-site safety risks.
6. Automated Product Assembly
Companies that have manufacturing processes can adopt different ways to use automated product assembly. From large to small scale, automated product assemblies are the norm in 2023. Remember that automated assemblies are not just limited to Tesla.
Examples: CV helps FMCG companies generate 3D design models, identify/track various product components, guide human and robot workers, and maintain standardized packaging. In manufacturing, automated product assembly uses AIto make assembly processes more accurate and efficient.
Computer vision systems direct on-site employees and robotic arms to assemble different components of a product faster. 3D modeling is the key to make sure product assembly is precise, reduces errors, accelerates production, and monitors different parts.
Electronics manufacturers also use this technology so that they can automate their assembly lines and develop precise consumer-based products like smartphones and tablets. For example, vision systems validate and affirm the proper placement of small components. It can include connectors and microchips that electronics manufacturers use to create high-end cameras. It’s an excellent way to meet specific product requirements and maintain high standards of quality control.
7. Quality Control on the Production Line
CV has become fundamental for manufacturers and FMCG players to improve and maintain high-quality control in their product lines. The traditional approach used to take a lot of time and involved endless errors. This tech has changed things for good. It allows manufacturers to easily inspect and pinpoint defects in the manufacturing process in real time.
Examples: Semiconductor manufacturers utilize CV algorithms to find defects in produced microchips. So, for each chip, it takes high-resolution system cameras to capture high-resolution images. Next, the specialized software inspects images and spots issues like irregularities and cracks.
Moreover, these systems can automatically detect faulty chips and ensure they’re not part of the production process. It helps manufacturers produce high-quality components in consumer electronics. On the flip side, food processing plants also use computer vision to check the safety and quality standards of their food products.
It involves integrated AI algorithms in cameras to detect issues like discoloration and foreign objections across product lines. And if any product doesn’t meet food regulation guidelines, it gets out of production. It also makes product classification and maintenance easier without compromising safety and quality standards.

8. Packaging Process Automation
Like quality control on product lines, FMCG companies use CV to automate their packaging processes. It makes packaging a multifaceted product line faster and helps companies maintain consistent efforts.
Examples: Beverage bottling facilities use this technology to check the labeling on the bottles before filling. In fact, they use the same systems to spot defects and imperfections within the glass. It could be wrong labeling, mislabeling, or a crack in the bottle.
Automated machinery continues to be a wonder for consumer bottling plants where on-site managers can discard defective products or make changes in real-time. It’s also an excellent way to reduce waste and maintain high-quality products.
Pharmaceutical manufacturers also use CV to ensure different medications are packaged accurately. Such solutions help pharma manufacturers ensure the packaging and dosage of capsules/pills are correct.
It is the best way to make sure each package has a precise dosage of medication and proper packaging at the same time. The pharmaceutical sector needs this level of precision to meet regulatory compliance requirements and ensure the safety of patients.
9. Equipment and Production Line Monitoring
In the manufacturing landscape, tracking equipment and product lines is common, and it works all thanks to AI solutions . Manufacturers use these systems to consistently track the activity of their production lines and machinery. Consequently, it allows manufacturers to spot anomalies, optimize schedule maintenance tasks, and prevent potential production failures.
Examples: Manufacturers that use heavy machinery use object detection to keep an eye on their equipment condition. It involves using cameras that record machinery and equipment performance information. This data can include wear and tear, vibrations, temperature, etc.
AI-powered cameras analyze data to anticipate whether or not it will need maintenance. Analyzing the same information also helps manufacturers figure out how they can make their machinery use more efficient and minimize unexpected downtime.
Similarly, steel manufacturing facilities deploy computer vision to maintain high-quality control in steel production. It also involves using high-speed AI-powered cameras to record images of the processed steel rolls in the production line. After that, algorithms analyze images and identify surface inconsistencies or other issues in the steel. This is the standard to produce high-quality steel products before shipping them to consumers.
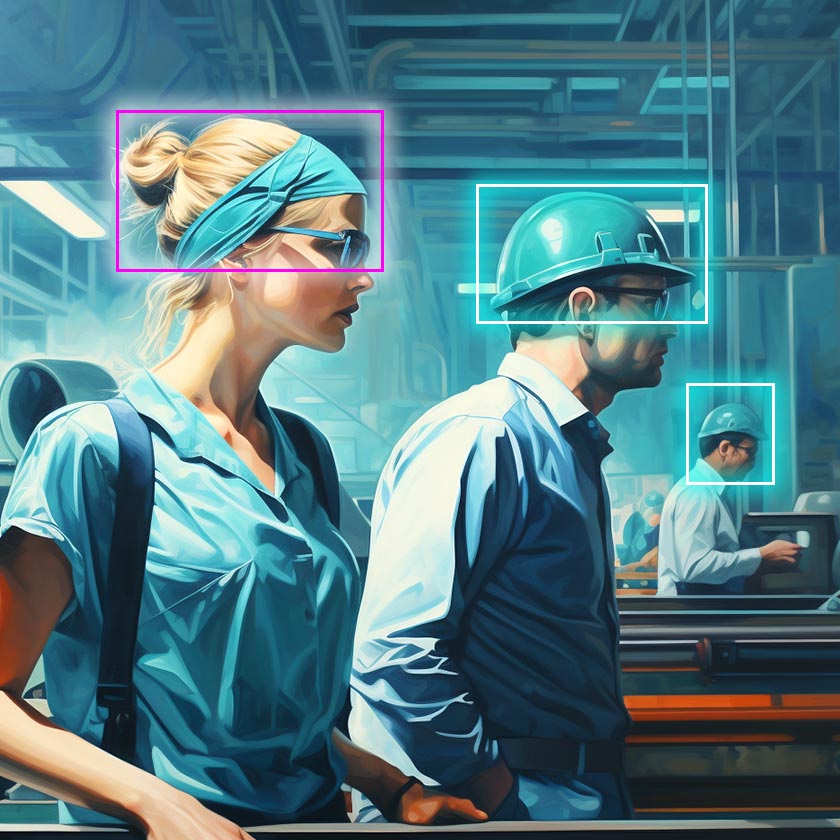

10. Safety Equipment Control
For manufacturers, one of the best applications of computer vision is to use it to track the use of PPE and comply with basic safety regulations to continue production processes.
Examples: In construction, manufacturers pair their equipment with AI systems so that workers are safe on-site. It requires construction workers to wear a protective safety helmet. However, these smart helmets integrated with AI-powered sensors and cameras can easily track and backtrack the use of PPE, like face masks and safety goggles.
So, if a construction site worker fails or forgets to wear essential safety gear – the integrated system within the helmet will send an alert and inform the workers to meet standard safety protocols and compliance.
If a worker is not wearing the required safety gear, the system can issue alerts and notifications to ensure compliance with safety regulations. The same technology works wonders for aerospace manufacturers.
It involves using dedicated system tracking tools to not just track workers’ performance on complex tasks – but also make sure they follow through fundamental safety regulations like wearing protective gear. If a safety violation comes into play, the system will alert supervisors through notifications. It will allow on-site supervisors to intervene without delay and prevent potential accidents.
Logistics

Logistics is one of the beneficiaries of computer vision tech. It allows logistics and supply chain companies to improve efficiency, heighten security measures, and take automation efforts to make the transformation of goods seamless.
The logistics and supply chain industry has become more dynamic over the years. In fact, distributors now opt for highly efficient methods to transport goods.
One of the perks of using CV in logistics is that it allows distributors and supply chain partners to cut back on costs, enhance security, and consistently improve efficiency. It continues to transform the logistics sector and has made it possible for most logistics and supply chain players to gradually let go of conventional logistics practices.
With computer technology, logistics partners can interpret and deduce visual data on a global scale. It includes using sensors and cameras with internal software to process videos and images. It’s an intuitive and efficient way for logistics and distribution companies to make data-driven decisions.
Let’s check out key applications in the logistics landscape:
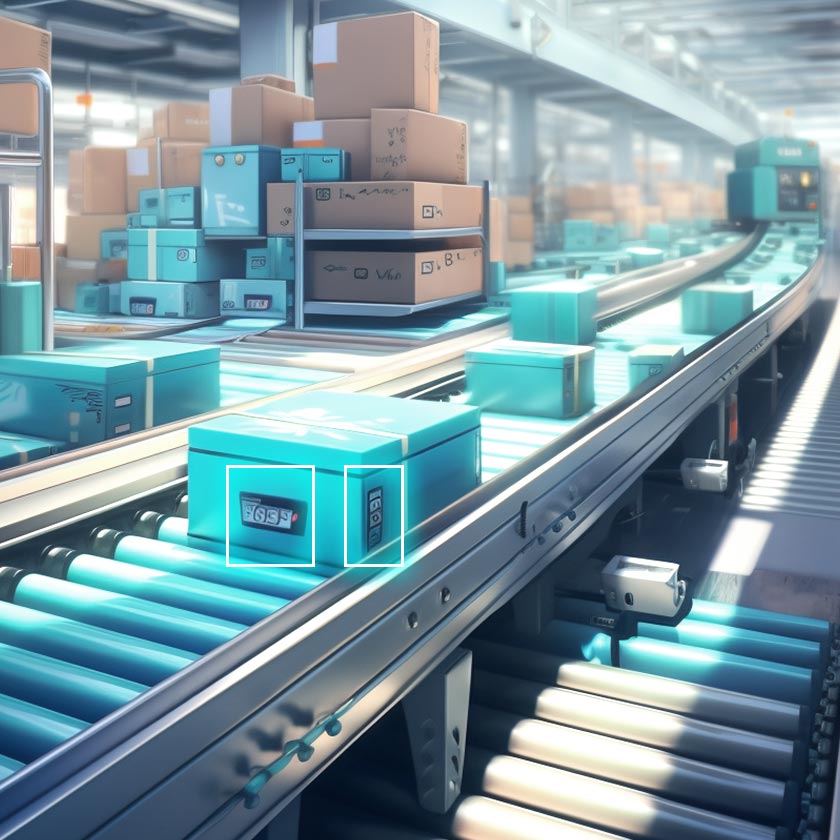

11. Automated Sorting Systems
Automated sorting is foundational to modern-day logistics operations. Computer vision has become the crucial player to make sure parcels and packages get efficiently routed to desired destinations. The best part is that this approach streamlines and centralizes the entire logistical process.
Examples: A major courier company like FedEx sets up a perfect standard. It uses this technology to thoroughly organize its facilities. It utilizes fast cameras to monitor packages when they move to conveyor belts. Part of it has to do with how efficiently every logistics company uses AI algorithms to analyze visual data and spot labeled packages.
Similarly, logistics companies can extract other information like zip codes and pinpoint locations. This, in turn, makes routing automated and allows logistical partners to find and reach their destinations faster and with the utmost precision. Computer vision also helps logistics and supply chain companies speed up delivery timelines, improve customer satisfaction, and leave little to no room for errors.
On the other hand, a top-tier eCommerce company like Amazon also makes the most out of CV technologies. Mostly, the company uses the technology to prioritize and classify a multitude of packages. The common parameters of classification revolve around weight, size, and delivery deadline.
The computer vision system paired with image analysis makes it possible for logistics experts to direct packages and spot characteristics ideal for different loading areas and conveyors to speed up the distribution process. This process helps Amazon make its logistics processes more efficient and deliver speedy results.
12. Inventory Tracking and Management
Inventory tracking and management have to be accurate to have proper availability of goods to meet high demand. With computer vision solutions – logistics companies gain insights into the state of their products and inventory thresholds in real-time.
Examples: Most retail distribution companies and dedicated centers use computer vision systems to be on top of their inventory management. It involves the strategic and accurate placement of cameras to scan QR codes and barcodes on different products when they move to the facility.
One of the best aspects of these cameras is that they consistently and automatically update inventory levels. It allows companies to make sure they have the stock to ship and avoid dealing with overstocking and understocking. Not to mention, overstocking and stockouts cost companies a lot of money.
You can also find a good example of flawless inventory tracking and management in the supply chain of fresh produce. CV is a savior for the food industry to ensure perishable goods get shipped in ideal temperature conditions and refrigerated transportation. It involves using specialized camera systems that monitor temperature levels. These camera systems are AI-powered and can analyze a plethora of data in the blink of an eye.
However, if there is a sudden change in temperature range, these camera systems trigger alerts and notifications to supply chain partners. This allows companies to take prompt actions and preserve the safety and quality of fresh produce throughout the transport. And all it takes is to readjust the temperatures within concentrated refrigerated space to ensure perishable goods are high-quality and safe to consume.
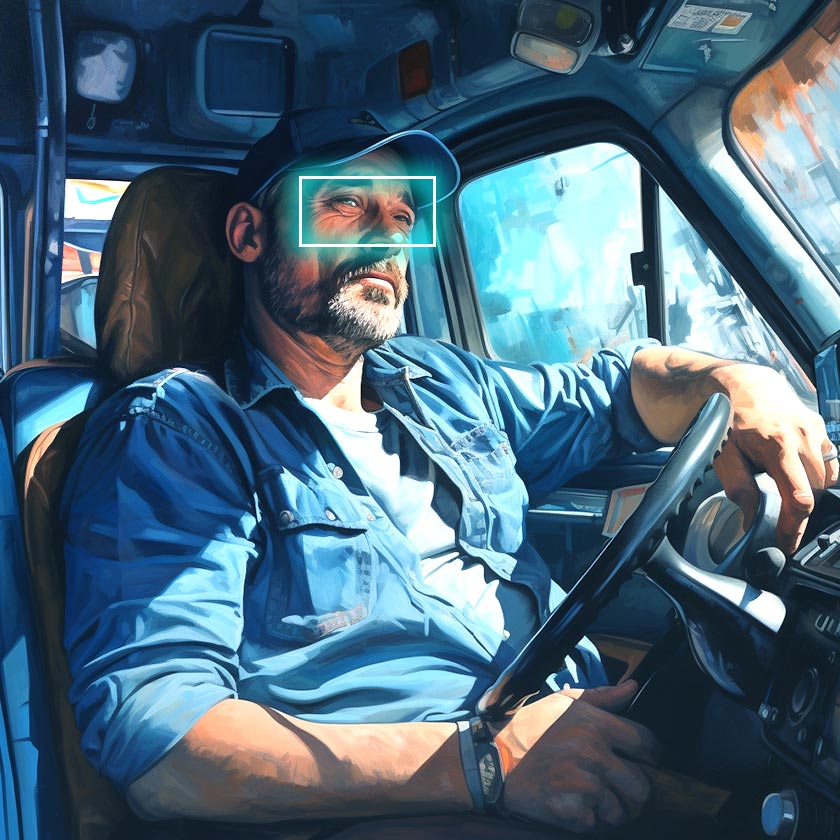

13. Driver Support and Fleet Management
Logistics partners that use vehicles focus a lot on efficiency and safety. In fact, these are the key drivers of maintaining solid logistics operations. With computer vision solutions, logistics companies can optimize fleet-based operations and maintain high safety standards.
Let’s look at some real-world examples:
Examples. Trucking companies pair their vehicles with advanced CV cameras so that they can track drivers’ behaviors. These dedicated systems are pre-trained so that trucking companies can quickly identify common signs of distractions and fatigue among drivers.
Ordinarily, tailgating is quite common among truck drivers. And the technology allows trucking companies to maintain safe driving practices. So, if there is some odd behavior and tailgating by a truck driver, the fleet manager receives a real-time alert and then takes prompt action.
The fleet manager usually reaches out to the driver to inquire about the issue and assigns a break. It sounds simple – but a proactive approach is the key here to make sure there’s no risk of on-the-road accidents and maintain road safety at all times for truck drivers.
Public transportation also utilizes similar computer vision systems to maintain the safety of their fleet. It involves installing internal CV cameras so vehicles can record occupancy and passenger count data in real-time.
But this is where efficiency and safety play out – data gets routed and optimized to meet predefined scheduling. These algorithms work around the clock to make sure passengers using public transport are safe. Most importantly, these algorithms in cameras can spot safety hazards and dangers in overcrowded places and make sure the drivers maintain safe social distancing.

14. Dimension and Volume Detection of Goods
Efficient and cost-effective transportation and cargo loading comes down to whether or not the companies accurately measure the volumes and dimensions of their goods. With object detection, this process becomes easier and allows logistics companies to review generated precise measurements to ensure cargo space is fully optimized.
Examples. Logistics and shipping enterprises leverage computer vision technologies to document and measure the dimensions of packages accurately. These companies use high-resolution AI-powered cameras to get razor-sharp images of packages from various angles.
Next, companies use AI software tech to analyze multiple angles, which makes it easier to calculate parcel dimensions with a high degree of accuracy. Logistics and shipping companies use this data to optimize the process of loading containers. It is the best way to maximize cargo space efficiently and minimize shipping expenses.
Accurately measuring dimensions doesn’t solely apply to shipping companies – airlines also use algorithms to calculate the shape and size of processed baggage. It allows airline companies to scan passenger bags and requires manual inspection if an item exceeds the standard size limit.
It makes the boarding process faster and ensures there are no delays because of oversized luggage. Most importantly, it makes the passenger experience smooth and influences them to travel more regularly, which is a huge win for airline companies.

15. Infrastructure Security Monitoring
Logistics operations require continuous security maintenance to safeguard goods and ensure a smooth supply chain and operational flow. Computer vision helps logistics companies improve their security tracking abilities in different logistics environments.
Example. Shipping thermals use CV-supported surveillance systems as part of their monitoring strategy to track cargo handling. Similarly, rail networks use the technology to track complex railway infrastructure like bridges and tracks. Both involve using AI-powered cameras to detect anomalies like potential track issues, safety hazards, and authorized access.
Healthcare

Computer vision applications in healthcare have become quite mainstream. However, a lot depends on hospital or healthcare institute staff to make sure the tech complements different aspects of operations.
The fact is that the healthcare sector is at the forefront of adopting AI-powered automation solutions. It’s 2023, and the healthcare sector is going through another transformation.
Let’s take a look at essential computer vision applications in healthcare with a few examples:

16. Disease Diagnosis through Medical Imaging
Medical imaging is the most common example of the healthcare sector not just jumping on board tech ride – but embracing it in full force. The rise of machine learning and deep learning continues to work in favor of the healthcare landscape. It’s the efficiency and precision of modern-day disease diagnosis that continues to make healthcare practices advance.
Disease diagnosis ties together with medical imaging like CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays. With computer vision, healthcare facilities can use image analysis to improve diagnostic processes. Medical imagining paired with this technology is a crucial aspect of today’s healthcare system.
Examples. Many healthcare programs now utilize 2D images and AI to get 3D format images. It allows physicians and doctors to pinpoint issues with a lot more accuracy. Microsoft’s InnerEye solution is a common example. Healthcare institutions use it to find abnormalities and tumors in X-rays.
All it takes for radiologists is to move scanned images to this program. After that, the software generates surface-level measurements of different ligaments and organs within the same image. After a thorough examination, radiologists can easily mark abnormalities and tumor areas and draw an informative and logical conclusion.
You can look at this tech through the lens of detecting breast cancer. Radiologists use CV to find out minor abnormalities within mammograms that hint at potential cancerous growth. The key is to use a solid image analysis and integrate it with a computer vision solution to detect the minute issues. This allows radiologists to make accurate and prompt diagnosis.
It’s a transformative technology that saves a lot of lives and has become integral in the healthcare industry. Dermatologists also use AI to review imaging of skin pigments and lesions. Dermatologists compare images and run them through an internal database to find the skin condition.
Internal systems help dermatologists accurately assess the severity of the condition and make professional diagnosis. It could be an early-stage skin cancer or melanoma. Nonetheless, detecting such health issues early on improves the chances of getting immediate and accurate treatment for patients.
17. Monitoring Patients in Intensive Care and Inpatient Units
When it comes to inpatient wards and ICUs, hospitals and healthcare facilities use computer vision solutions to consistently keep an eye on patients’ health, improve the quality of care, and mitigate some of the workload off of administrative staff.
Examples: Intensive Care Units depend heavily on CV integrated cameras to continuously track patients’ vital signs like heart and respiratory rates. With this technology, healthcare professionals can spot even minor changes in vital signs in real time.
In fact, any change triggers an alert that medical staff receives and allows them to make proactive decisions before the patient’s condition gets worse. Monitoring vital signs in real-time directly minimizes medical errors and improves the quality of patient care and chances of recovery.
The same rules come into play for inpatient units to prevent or detect a health issue. So, if there’s an elderly patient at risk of falling, it sends alerts to nursing staff so they can act on time.

18. Analysis of Medical Data and Research
Computer vision doesn’t just support advanced clinical diagnosis – it helps medical professionals perform in-depth research. It involves automating data extraction and analysis. It means medical experts don’t have to dive into the rabbit hole of huge datasets and medical imaging to perform analysis.
Examples: Analysis of medical data and research is integral in pharmaceuticals. It involves using AI algorithms to automate comprehensive drug analysis. It allows pharma companies to speed up the research process and process a multitude of data that involve clinical trials and experiments.
Moreover, it speeds up the process of finding the “right” drug and even unearth new discoveries. Neuroscience researchers use computer vision regularly to analyze MRI brain scans. It involves using dedicated AI-powered algorithms trained to read, analyze, and track complex brain structures.
It’s a great way to find valuable insights about major healthcare diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. This tech is mostly used to better understand how fast the disease progresses and find the most suitable treatments for the patients.

19. Real-time Assistance in Surgical Procedures
Computer vision tech is now part of the medical operating processes. It helps surgeons and other healthcare specialists navigate complex procedures in real time.
Examples: Minimally invasive surgical processes involve using CV solutions. It makes it easier for surgeons to keep up with the movement and position of surgical instruments.
Precision-based tracking now revolves around many software solutions, but the use of this technology is at the top. And that’s because it gives surgeons more navigational control over the patient’s body. It doesn’t just minimize potential complications but improves the likelihood of a successful surgery.
It means surgeons can leverage heightened precision-based tracking through computer vision to perform complex procedures. From the perspective of patients, it shortens the overall recovery period. Another example is using it for robotic-supported surgeries to have a magnified, sharp, crystal-clear view of the entire surgical area.
Surgeons can also count on the algorithms to automatically change camera focus and angles to optimize the field of vision. This technology heightens the skills of surgeons and makes the surgical processes more precise and efficient at the same time.
20. Enhancement of Medical X-ray and CT Image Quality
Computer vision solutions are crucial to enhance the quality of CT scans and X-ray images. In the 21st century, these systems are fundamental to make spot-on diagnosis and strategically provide treatment planning.
Here are a few common examples:
Examples: It is common now for radiology departments to use CV and improve chest X-ray quality. These systems use algorithms to increase contrast, optimize image sharpness and clarity, and minimize image noise. It allows radiologists to detect minor to major abnormalities and leads to accurate diagnosis. It can include lung cancer, tuberculosis, pneumonia, etc.
In the context of CT imagining, the same technology is used to reduce the dose of radiation for scans without compromising image quality. CT scans have high exposure to radiation of ionizing. So, with minimal radiation dose, patients are safer. Computer vision solutions also make changes to exposure parameters to optimize internal scanning procedures.
The system might adjust elements like tube voltage or tube current to stabilize the image. It’s a practical way to reduce exposure to radiation and maintain high-quality diagnostic images. Safe and accurate CT scans are incredibly beneficial for patients who undergo repetitive imaging. It can be a treatment response review or tracking chronic conditions.
Automotive Industry
For the past few years it feels like the automotive sector has been going through a major transformative change. And it’s not just AI – but the integration of machine learning is in full force. The major driver is computer vision tech. Whether it’s safety features or autonomous navigation, quality control and manufacturing speed are crucial in the automotive landscape.
With integrated object detection, auto manufacturers are changing the way you build and design vehicles. Auto companies’ main focus is improving user experiences and building highly interactive vehicles.
Here are main applications of the technology in the automotive industry with some of the most hallmark examples.

21. Autonomous Navigation and Parking
CV solutions are empowering and allowing today’s autonomous vehicles to efficiently and safely park and navigate controls. Typically, it can be quite challenging to find a suitable parking space. With integrated algorithms in cars, drivers with different driving experiences can find parking easily.
Examples: Sensors with built-in network allow vehicle drivers to track the available space. The same systems can determine parking hours and times. This is also a realistic approach to improve traffic control and navigation.
Vehicles now come with built-in navigation, and AI-powered solutions make it easier to spot free parking. The same systems also alert drivers about traffic jams ahead of the road and notify drivers when they forget to park their vehicles.
No wonder arenas, stadiums, and airports now use computer vision to have a balanced flow of traffic, minimize potential barriers, and allow visitors to roam without being a security risk.
Autonomous vehicles with integrated CV cover radar, LiDAR, and cameras, which makes it a no-hassle process to perceive their environments. Integrated computer vision systems can also analyze comprehensive datasets in minutes and help auto vehicle owners identify and monitor on-the-road objects. This primarily includes pedestrians, other road signs, and other vehicles on the road.
The AI solution consistently analyze and contextualize visual data so autonomous car owners can accurately steer, brake, and accelerate. In essence, it’s all about helping the auto driver navigate complicated surroundings and make the driving experience more accurate and safe.
22. Accident Prevention
Traffic control authorities now use computer vision to detect traffic incidents automatically. Of course, video surveillance has come a long way. However, manual video surveillance involves a lot of time and requires human labor.
With automated accident prevention, it is much easier to spot traffic accidents and increase response time in real time. And AI-powered solutions complement these applications.
Examples: Today, you can detect multiple kinds of accidents, and all it takes is to connect intelligent transportation system cameras. When you pair vehicles with intelligence sensors, the process of detecting and responding to potential accidents gets simplified.
So, when these AI algorithms continuously warn/alert vehicle drivers about dangers on the road, it becomes possible to avoid a lot of severe accidents and save more lives. Traffic incidents that get reported the most are driving too low or too fast, pedestrians directly entering the traffic road, or blocking cars. This is where computer vision works – they aid vehicle drivers to not make the wrong turns and keep a safe distance from on-the-road debris.
Whether it’s lane departure or preventing forward collision, CV is used to spot obstacles and vehicles in the vehicle’s path. These systems can automatically anticipate a likely collision and visually and audibly alert drivers to hit emergency or automatic breaks. Thanks to AI algorithms, there’s been a significant reduction in rear-end collisions.

23. Adaptive Car Lighting Systems
Adaptive vehicle lighting systems utilize computer vision to maximize the output of headlight beams. This significantly improves visibility and makes driving more accurate and efficient.
Example. With adaptive headlights, drivers can count on automated adjustments of light intensity and direction based on steering angle and driving speed. Adaptive car lighting systems review road conditions and monitor car’s movements.
This makes it possible for these systems to illuminate headlights brighter and keep the driver safe ahead of every twist and turn. Car drivers can count on these systems to change the road trajectory when taking a turn without losing visibility at nighttime and enjoy a safe driving experience.

24. Driver Behavior Analysis and Accident Reduction
Computer vision can deduce driver behavior. This is a great way to minimize accidents that stem from drowsiness, aggressive/reckless driving, and distractions. Driver tracking software use cameras to monitor the facial expressions, head position, and eye movements of the driver. This combined system can find any signs of distraction, fatigue, or drowsiness.
If the driver is experiencing any of these issues, it will send an alert to redirect the driver’s focus on the road. In fact, these systems are quite compact and useful for reducing the frequency of on-the-road accidents. More and more auto manufacturers want to integrate these systems to support individuals with impaired hearing.
Example. Fleet management software pairs computer vision to better analyze the complex behavior of drivers. These systems monitor and deduce the driver’s behavior based on harsh braking, aggressive acceleration, and speeding. Fleet systems then send analyzed data to fleet managers. Next, fleet managers can put in place training programs to minimize wear and tear, reduce accidents, and improve driver behavior.
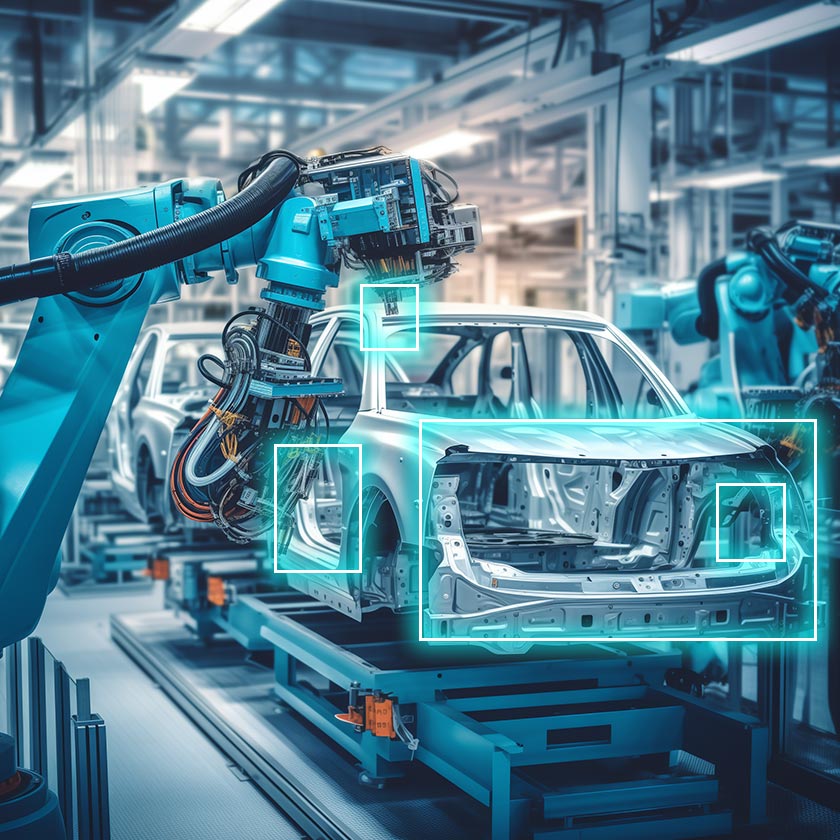
25. Quality Control during Vehicle Production and Assembly
From the start of the production to assembly line, quality control is paramount to auto manufacturers. Computer vision helps auto manufacturers maintain high-quality standards throughout the production process.
Example: Robotic automotive assembly lines now utilize CV. This makes it easier to assess the vehicle’s interior and exterior. It involves using high-resolution AI-powered cameras to take the vehicle’s images as it moves through each phase of the assembly line.
This usually involves finding defects like interior flaws or disjoined body panels. So, if a problem of a similar nature pops up – the internal system detects and flags it and moves it along for the manager to take some kind of action.
Consequently, it keeps the assembly line in check and helps auto manufacturers maintain high-quality standards in every production vehicle. Expect computer vision to evolve in the automotive space. As a result, it would allow auto manufacturers to build and design cars with more safety features and help drivers stay safe on the road.
Agriculture

In the last century, of course, the agriculture sector has had traditional advances. However, like other industries, things are changing for good in the agriculture industry, and part of it has to do with AI contributions.
From New Zealand to the Netherlands, farmers now use AI models like computer vision to track their yield and crop, detect plant diseases, monitor the health of their livestock, automate harvesting, and accurately forecast weather conditions.
The technology has made headlines in the agriculture sector with consistent adoption. After all, farmers understand that AI-powered disease detection and automation capabilities will allow them to not just protect their crops but scale up the production.
Let’s check out the most famous applications in agriculture with practical examples:

26. Plant Growth Monitoring
Plant growth monitoring is done through aerial imaging and surveys. It involves using drones to monitor the environment and the land scene. It is getting a mainstream approach for most farmers and continues to transform the agricultural landscape as we know it.
Examples. Farmers now use computer vision to take advantage of drone-extracted image data to remotely monitor livestock and crops. At the same time, farmers can collect more information about soil composition and field environment.
Today monitoring livestock health has become a walk in the park for farmers. Computer vision allows farmers to track their animals and unpredictable actions in real time. This also makes animal counting easier than manual counting.
Most importantly, this technology helps farmers track birth monitoring and spot unusual behavior or diseases in livestock. Farmers can combine video and image data to suit specific environments and add sensors to have a good idea about ventilation and temperatures. But that’s not all – these AI systems also give farmers accurate insights about animals’ changing water, food needs, and health conditions.

27. Disease and Pest Detection
Early pest and insect detection allows farmers to take proactive action rather than take measures when it’s too late. This allows farmers to protect their crops better and minimize the potential damage. Farmers now use camera-powered crop tracking system solutions.
Examples. More and more farmers now depend on these systems to count threatening insects, classify insects, and spot more insects that are within the surroundings of the crops. Automated pest and insect control helps farmers save hundreds and thousands of dollars in pesticide products.
Farmers can also use computers to find out crop diseases and take immediate action. Farmers are now tech-oriented and use smart devices to detect diseases and make sure there’s little to no crop loss. Computer vision in agricultural settings depends on publicly available datasets. The AI-trained data consists of diseased and healthy plant leaves. However, this is not where the process ends.
Experts use this data to train AI and build a complex neural network. The trained datasets allow farmers to easily detect crop types with potential diseases. With these AI models, farmers usually get as high as 99% accuracy when they run tests.
Image classification and segmentation tactics are crucial parts of detecting plant diseases. It involves a genetic algorithm that supports data. What’s exciting is that farmers now use smart devices and leave it to the AI to analyze complex quantitative and qualitative data in a matter of seconds.
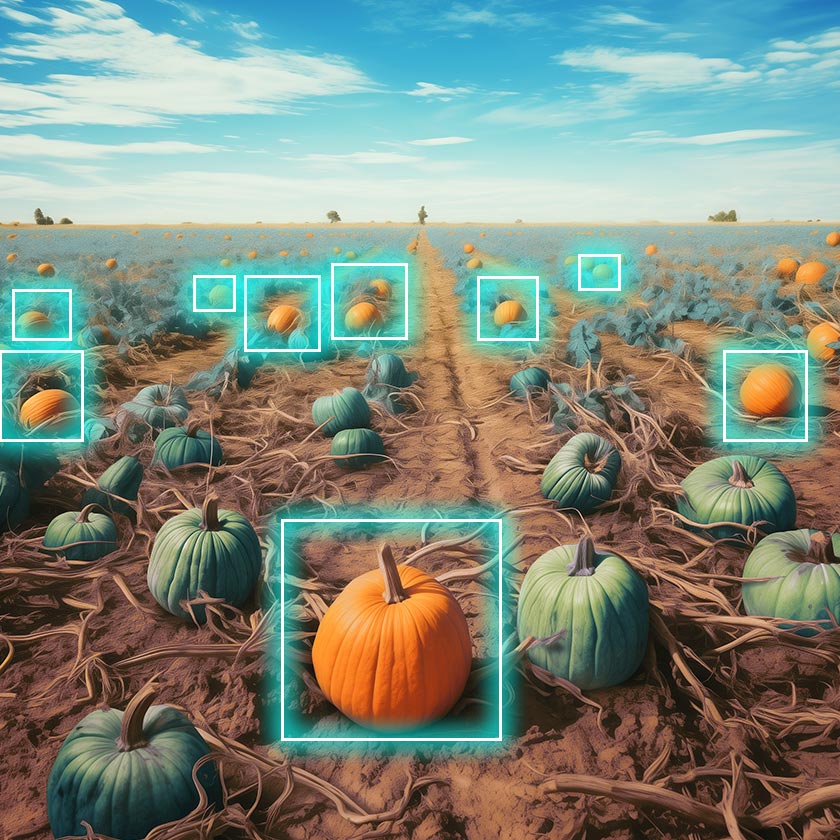

28. Determination of Agricultural Crop Maturity
Finding out the exact harvest time is part of the process of determining crop yield and quality. With AI algorithms, farmers consider parameters like the texture, size, and color of their crops to review their maturity.
Examples. It is a highly precise and mechanical process for farmers to figure out specific crop maturity. And AI algorithms bring something to the table. It allows farmers to harvest crops at ideal times to increase ripeness and produce more to meet high market demand.
Fruit Ripeness review is a systematic process, and when farmers bring AI algorithms into the picture – assessment takes less time and paints a clear picture. If you take the fruit industry, for example, the use of computer systems has become common to review the ripeness of various fruits like apples, oranges, grapes, and bananas.
It’s all about analyzing images and analyzing fast enough so that farmers can figure out the best time to harvest based on the size, firmness, and color of the fruit. Computer vision is still a relatively new tech, but it helps farmers pick fruit at peak time, which improves their shelf life and taste.
Consider crops like rice or wheat – the hallmark cereal crops. Farmers use computer vision to assess the grains’ maturity. Experienced farmers run image analysis and configure systems to check elements like the size and color of the grains. It allows farmers to harvest in an ideal timeframe without shooting arrows in the dark. It helps farmers harvest accurately and produce high-quality grains. It makes it possible for farmers to sell their high-quality grain for top-tier rice products or baking bread.

29. Irrigation and Fertilization Optimization
How farmers manage their resources makes a huge difference and directly determines whether or not they’ll have a sustainable field of crops. With AI solutions, farmers can make their resource planning and management a lot more efficient.
Examples. Computer vision algorithms allow farmers to follow the best practices of sustainable agriculture. For starters, the solutions help farmers easily review crop health and soil moisture levels. These parameters help farmers optimize the fertilization and irrigation of their crops.
Farmers use CV to adjust these parameters to cater to their specific crop needs. It can be adjusting the fertilizer usage or reducing water usage to achieve a high yield. Soil moisture management becomes easier with the technology.
Farmers can use this information to make irrigation scheduling highly accurate, ensure crops get suitable hydration, and there’s minimal waste of water. Nutrient distribution is another example where the technology simplifies the process. Automated drones now feature computer vision and allow farmers to review the nutrient distribution in fields.
AI helps farmers take multispectral shots and assess plant health parameters. Farmers can use these valuable collective insights to change their fertilizer application rate around multiple crop areas. It is an efficient way to make nutrient distribution efficient and mitigate the environmental impact at the same time.

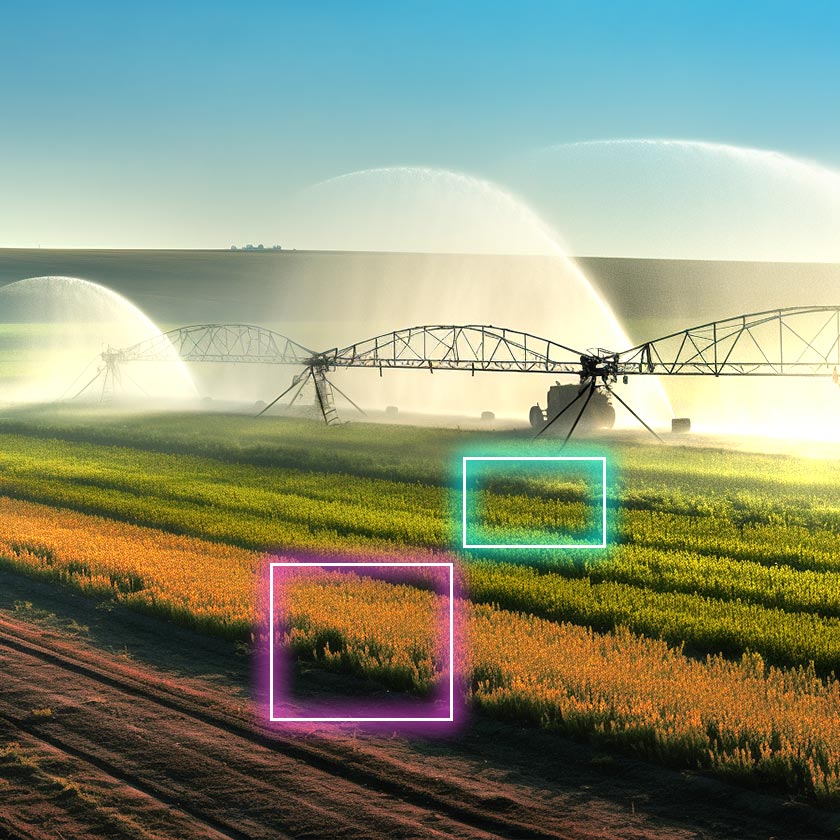
30. Harvest Time Prediction
Computer vision does more than help farmers track crop growth – it allows farmers to anticipate the most suitable harvest periods. The idea to analyze and make informed decisions in real-time is not a far-fetched reality – AI systems have made it possible for farmers.
Examples. Farmers can use these systems to predict, harvest, observe, and spot the ripeness of fruits or the maturity of their grains. In outdoor settings, vision systems work around color ratings and use variables to help farmers figure out the ideal harvest time.
Computer vision also supports monitoring tools that are now fully autonomous and solar-powered and work in tandem with drone systems. It helps farmers get a peak at HD videos and images and better review their soil and crop conditions.
From North America to Europe, AI solutions can now gauge complex data based on the texture, shape, and color of the crops. High-definition sensor camera systems allow farmers to accurately track soil moisture and predict high yield.
When farmers combine CV with forecasted weather and historical data, interesting things transpire. Specifically, it allows farmers to accurately predict the optimal time to harvest. It is important in the wine industry, where these systems help farmers assess grape clusters’ sugar content and color.
Computer vision considers weather forecasts to determine the exact time farmers should harvest in order to produce wine with specific attributes. It’s 2023, and scalable crop farming is on the rise. Farmers use AI models to predict and track crop growth across fields.
It does, however, take consistent monitoring of how the plan develops and matures. But this process allows farmers to figure out exactly “when” their crops will mature. Farmers also use this data to make their harvest schedules more efficient and don’t assign more resources than they have to.
Energy and Ecology

The energy landscape has had significant changes in the last decade. Energy leaders now recognize the relevance of new tech solutions like AI-powered automation and consistent innovation to maintain a competitive edge in the market.
Today, the electric power sector is moving from traditional practices to reliable, resilient, and robust grids. And since computer vision is a top-tier AI tech – it allows energy companies to disrupt the power and utilities sector. The next-gen artificial intelligence solutions are here and now to help energy companies become safer and more efficient than ever.
Examples. In terms of CvV, the most practical and famous applications revolve around monitoring, surveillance, inspection, and detecting foreign objects. It also covers security, assessing operational behavior, detecting abnormal situations, and having smart control over personnel on the field.
In the coming years, the energy industry is bracing to face new challenges and using computer vision and other AI-powered solutions to address such challenges. It includes promoting clean energy, making grid networks more resilient, predicting extreme weather conditions, and maintaining top-notch security.
However, the key challenge for energy players is to overcome all these issues without increasing operational costs. Energy companies now want to have a global impact and use disruptive tech to stand out. The transformation of the energy sector has already started – and AI-powered solutions are at the forefront.

31. Equipment Monitoring and Fault Diagnosis
Power companies continue to implement deep learning artificial intelligence models to have seamless equipment detection and protection. Energy companies usually work in uncertain and dangerous environments, and this is where companies use automated inspections to improve safety management using protective gear like vests, helmets, and proper uniforms.
Example. Energy companies can use computer vision sensor cameras to automatically report and track misconduct or violations and take immediate safety measures. Vision-powered AI inspection doesn’t just help energy companies become more consistent – it cuts out the need for manual supervision. It’s a practical approach for energy entities to save valuable time and resources.
Once AI-powered vision technology is in place, energy companies can easily track and recognize the status of their equipment, like lighting arresters, capacitors, circuit breakers, transformers, and integrated electrical appliances in each substation.
Automated detection in the early stages also helps energy companies find out hidden dangers and potential failures and detect network anomalies. All these elements bring down the costs of maintenance and operations.
Computer vision allows energy companies to be objective, automated, consistent, and precise rather than rely on manual human inspection, which leads to more errors. The same rules apply when energy companies inspect oil rig machinery and equipment and review solar panels.
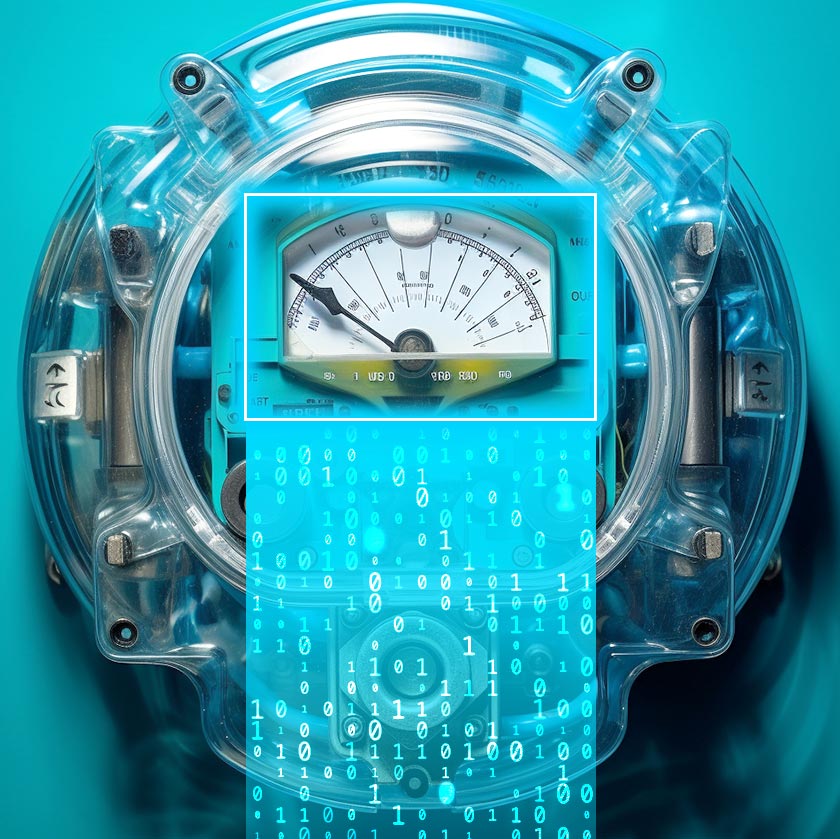
32. Recognition of Analog Control Elements
AI-powered vision is part of turning analog into digital processes. Specifically, vision systems are perfect for digitizing analog-based controls. Now, it can be, say, pointer position or lights detection, liquid position on transformer oil, or detecting position switch.
It makes automated meter reading possible. This means no human intervention to consistently monitor and collect data. Automated meter reading features predictive tracking and can spot inconsistent elements of equipment more likely to fault.
Example. The control room of a nuclear power plant uses object detection to track analog control panels. With computer vision, on-site reactor operators can make sure they’re making spot-on changes. It’s the best way to maintain secure and productive operations.
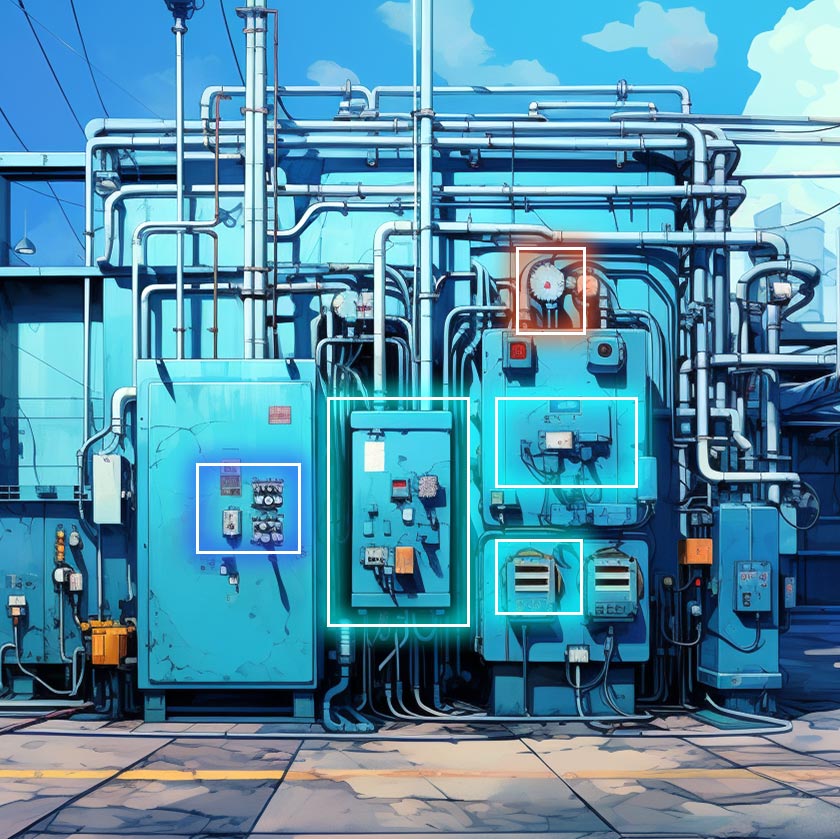
33. Safety Equipment Monitoring
In the energy sector, one of the main priorities of companies is to track equipment with a bigger safety net. In the industrial sense, worker safety matters, and the key to achieve that is tracking “how” employees exercise basic equipment safety practices.
And this is where deep learning algorithms shine. Energy and utility companies use AI-powered computer vision system cameras to spot any employee not wearing goggles, gloves, helmets, or any other important safety gear.
And if an employee is not compliant, it triggers an alert to make sure that particular worker follows standard safety protocols and to minimize potential accidents.

34. Infrastructure Safety Monitoring
Computer vision tech is perfect to track and assess infrastructure safety. And that’s because computer tech makes it easier to determine and avoid potential infrastructure risks.
Example. Checking the integrity of levee and dam is more straightforward through the technology. With AI, tracking becomes automated, and it allows you to review levees and dams’ integrity at all times.
The earlier the detection – the sooner you can take preventative measures. It is an ideal way to minimize potential dam failures that can mutate into an environmental disaster. In ecology, companies now use computer vision to detect potential forest fire.
This is a big deal when it comes to natural and ecological resource management. The idea is to use cameras and place them throughout the forest to quickly identify when there are flames or smoke. So, when and if this system detects a potential fire, you can count on automated alerts sent to firefighters to respond to the situation as soon as possible and minimize ecological damage.

35. Energy Consumption Optimization and Waste Reduction
Environmental sustainability depends on how far you optimize your energy consumption and minimize potential waste. Again, computer vision tech shines through and through. It allows energy companies to achieve their targets without tanking environmental sustainability.
Example. Computer vision helps energy companies to better manage and use resources and cut back on waste over a long period. In this case, the most obvious example would be the load balancing of smart grids. Energy distribution spans across networks, and artificial intelligence algorithms are a perfect tool to track power usage and detect patterns in real time.
Once you review data, you can continue to use vision-sourced AI algorithms to find a perfect balance between electrical load and power distribution. And it won’t just make the electric grid more efficient – it would minimize energy waste and allow you to do your part to make your energy infrastructure more sustainable.
Recycling and classifying resources automatically is another example across energy facilities. Object detection makes it easier to organize and automate waste materials. You can use AI-powered vision system cameras to classify glass, paper, plastic, etc. This allows you to play around with automation on a big scale and increase your recycling rates. It minimizes landfill waste and propels you to responsibly manage energy resources.
Oil and Gas Industry

In the modern-day gas and oil industry, detecting leaks and third-party issues is crucial. Otherwise, environmental hazards will spiral out of control. Companies can deploy vision tech to track gas and oil leaks. AI algorithms can pair perfectly with the camera to flawlessly review images and direct changes.
Example. Spotting things like changes in liquid flow and the temperate rate is to take prompt action before things get out of control. Plus, detecting leaks early on allows you to build a solid response mechanism. It allows you to mitigate environmental damage and saves you from paying upfront costs.
You can use the same vision technology to assess pressure vessels. This allows oil and gas companies to run soother drilling and refinery operations. When it comes to vessel surfaces, vision tech paired with HD cameras captures sharp images.
This makes it easier to identify issues like stress and corrosion. And when you’re able to detect such issues early on – it allows you to run safe operations and significantly reduce the likelihood of failures.

36. Leak and Defect Detection
If you want to safely transport gas and oil, you’ll need to consistently monitor, review, and make sure pipelines are not just efficient – but secure.
Example: Reviewing pipeline condition through CV becomes a simple process and makes it easier to check pipelines’ actual condition.
This also involves computer vision system cameras integrated with artificial intelligence algorithms and drones to capture exterior surface images of the pipeline. After that, it’s just a matter of reviewing analyzed images and spotting common signs of corrosion, infrastructure damage, or wear and tear. This makes prompt repairs and consistent maintenance relevant to not just avoid leaks – but to maintain the integrity of pipelines.

37. Pipeline Monitoring
Computer vision is perfect for keeping an eye on pipeline routes. It is even more critical when pipelines are in sensitive environments and difficult terrains.
Example. The approach to use this technology is more or less the same. It involves using camera drones with GPS to get the data and images so that you can evaluate potential risks. Potential intrusions can involve construction tasks or land movement. In any case, the key is to track pipelines consistently to make sure that they’re safe and comply with a specific environment.

38. Optimization of Drilling Rig Operations
The next time you see optimized drilling rig operations – understand that it’s all about how companies utilize their resources and cut back costs. Making drilling rig operations efficient doesn’t have to be complex.
Example. You can use computer vision to review drilling site images. Take your time to check the condition and see if there are any patterns of wear and tear. After that, the computer vision system would give you some suggestions on when you should sharpen or altogether replace your drill components. This style of optimization makes your drilling operations incredibly efficient and minimizes your downtime.
You can use the same tactic to use algorithms to run drilling-based fluid analysis. In fact, vision-powered sensors and cameras can accurately track fluid density and composition. Use rendered insights to make your drilling operations more effective – but also to empower operators to make the changes to reduce waste and improve overall drilling efficiency.

39. Resource Extraction Optimization
When you operate in the gas and oil industry, there’s no room for mistakes. In the gas and oil landscape context, resource extraction is all about maintaining sustainability and efficient processes with high accuracy.
Example. There’s a reason computer vision systems have become so instrumental in resource extraction and optimization. Part of the reason is that these systems offer valuable insights and speed up the decision-making process in real time. For instance, oil and gas implement the technology to monitor reservoirs.
Technically, it involves placing vision-powered sensors and cameras inside the reservoirs and wells to get accurate flow rates, reservoir conditions, and internal pressure. You can use this data to more than just improve decision-making – but optimize entire production processes. You can apply the same vision technology to seamlessly monitor and manage reservoirs.
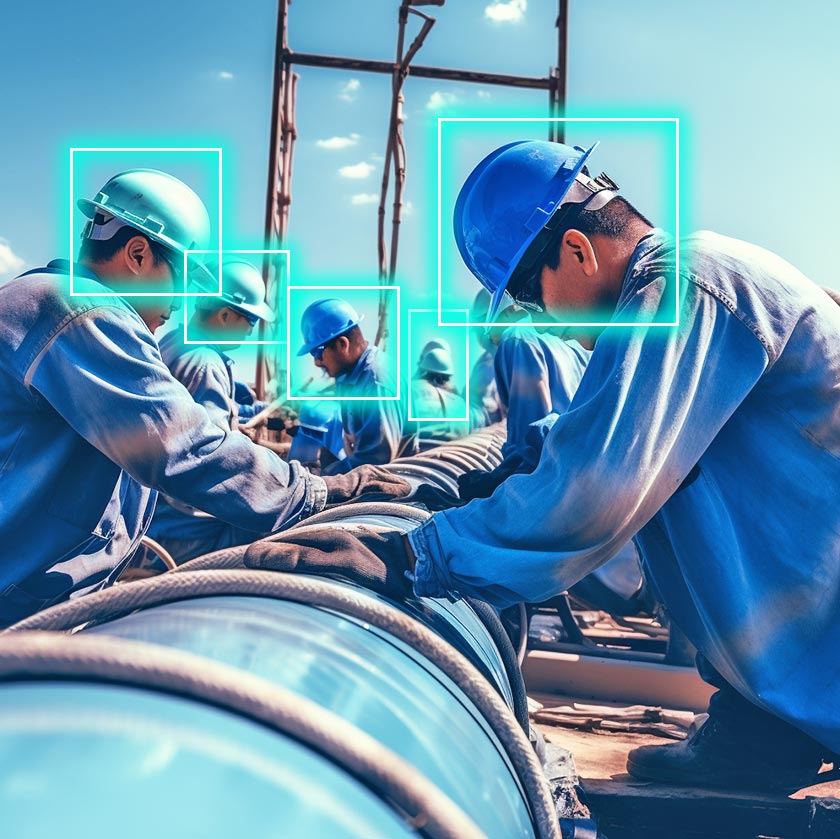

40. Safety Equipment Monitoring
It has become a fundamental practice to monitor equipment safely to improve workers’ protection and ward off potential accidents. This is one of those elements where operational conditions can get hazardous pretty quickly. And you want to make pre-planned and pre-defined measures to make sure workers work in a safe environment.
Example. PPE compliance doesn’t become a chore when you bring computer vision into the picture. You can use these systems in modern-day industrial settings and ensure workers use equipment safely. It’s not rocket science – vision systems use AI algorithms to affirm and reaffirm compliance practices and trigger alerts whenever there’s a non-compliance issue.
Systems essentially make it easier to recognize protective gloves and clothing. Similarly, vision cameras can easily spot whether or not workers are wearing helmets on-site with hazardous objects. And ensuring workers wear the compliant gear is paramount.
With vision cameras, it is easier to verify goggles and glasses so that workers are safe from potential hazards to the eye, like chemical splashes and flying debris. Vision-powered cameras and sensors also allow oil and gas enterprises to monitor emergency exit control and access and make sure respirator compliance and gas detection is around the clock.
Banking and Finance

Banking and financial service institutions have had major digital transformation in the last few years. With the rise of FinTech and more divisive banking practices, there are also now more cybersecurity risks. Addressing such issues in the banking and financial industry can get more complicated than in other industries.
For starters, it involves a lot more research and due diligence. Fortunately, AI algorithms and ML models have come to the rescue in the form of computer vision. Just like ML models are ideal for spotting objects, analyze motions, and track activities, the financial industry uses the technology to protect sensitive financial information using deep learning models.
This is a perfect AI solution for banks that offer a variety of financial services. There’s more to CV than just spot traffic violations – financial institutions use it to validate and confirm debit and credit card information. Computer vision tech is also great for detecting data patterns and visualize information to have precise descriptions of rendered services.
With a dedicated AI solution, banks and financial institutions can train large datasets using various deep learning tactics. This will allow banks and the service industry to automate financial processes. Computer vision models can also help the financial service sector in tasks like automated check processing, image fraud detection, and assessment of financial documents.

41. Automatic Customer Identification
Modern-day banking systems revolve around automated customer identification. It improves the internal cybersecurity of banks and the financial service sector and speeds up the process to onboard new customers.
Example: Computer vision allows banks and the financial service sector to easily confirm customer identities using biometric authentication. This decade is haunted by rising cybersecurity threats and attacks, and this means more pressure on banking and financial institutions to strengthen their current network security.
People now mostly use mobile banking apps to get most of the financial services they need through biometric verification. CV confirms biometric data and allows customers to access their bank accounts and make transactions or engage in other financial services.
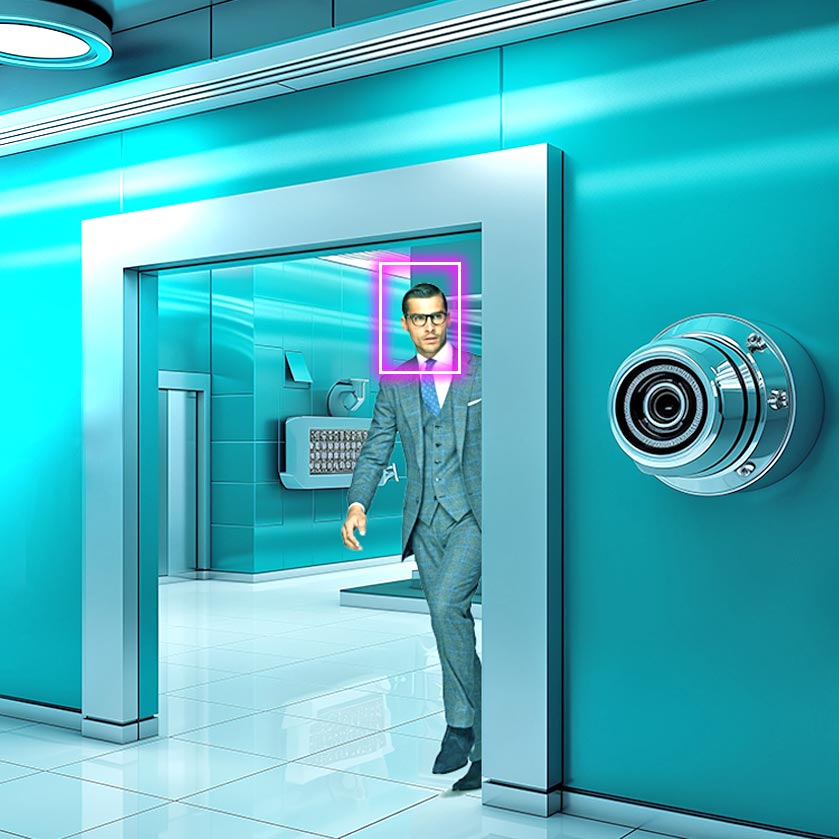

42. Access Control Systems
Control access systems allow financial institutions and banks improve the security of their vaults, data centers, and restricted workspaces.
Example: Implementing AI-powered facial recognition systems at bank ATMs is the most common example. However, access control through facial recognition for internal areas is also getting common. The goal is the same: use computer vision AI algorithms to authorize staff or confirm their identities.

43. Facial Recognition in Queue Management and ATMs
The banking and financial service industry has come a long way when it comes to using facial recognition tech to speed up ATM operations and queue management.
Example: queue management through facial recognition has become a standard practice in the banking and financial service industry. Facial recognition in place identifies and tracks customers who are in the queue. Banks position vision system cameras with facial recognition tech to make sure customers’ facial features match their bank account details.

44. Infrastructure Security
Cyber attacks are out of control, no wonder cybersecurity is the main priority for banks and financial institutions.
Example: Computer vision is an excellent solution for banks to protect the data of their virtual and physical branches. It’s a logical way to improve security, engage better with customers, and improve the banking experience.

45. Authenticity Recognition of Banknotes
Counterfeiting currency has been going on since the dawn of capitalism. However, technology has advanced enough to reach the sights of cybercriminals who use it to exploit banknotes.
Example: Computer vision allows banks to improve the security standards of their banknote authentication. It can automatically flag suspicious banknotes and direct them for thorough review. Similarly, banks use POS systems to authenticate transaction banknotes and validate them in real time.
Computer Vision Tackles a Multitude of Tasks Across Various Industries

Computer vision tasks are numerous, this technology effectively addresses challenges in diverse business processes for different industries. It outperforms human capabilities in terms of speed and accuracy, and remains tireless and eliminates the errors associated with human factors.
Computer vision simplifies data pipelines and workflows and allows businesses from different industries to drive more growth and innovation. You can tap into analytical solutions and build solid data pipelines to leverage these CV applications and use cases.