Nowadays, artificial intelligence is becoming an indispensable tool for retail trade. As reported by McKinsey, in companies, which use AI, revenue is increased by 3-5% and expenses are reduced by 15%. Solutions based on computer vision are particularly efficient. They computerise merchandise display, analyse customer behaviour and optimise product layout.
Despite general belief, to bring AI into retail sales, one does not require long-term projects taking months to implement. There are approaches that make it possible to launch such solutions in just one month or even several weeks. This article deals with three main scenarios for quick AI implementation in the processes of FMCG companies in order to improve performance without major investments.
Table of Сontents
How Artificial Intelligence Improves Business Processes in Practice

Artificial intelligence and computer vision are becoming indispensable assistants at retail outlets. They help to reduce service costs, to increase purchase amounts, and to predict customer behaviour more accurately.
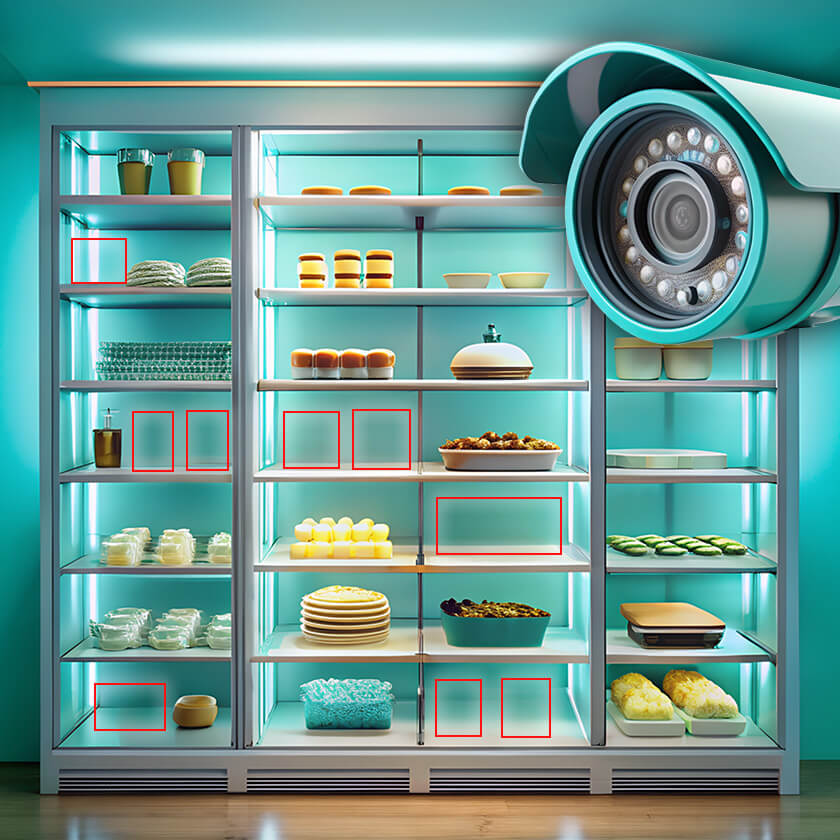
At points of sale AI solutions are used to check whether all relevant products are available on the shelves and to select the best places to place the products. If any product is stolen, the computer vision will see it and notify the employee in charge. In addition, AI technologies can show the map of customer movement across the retail space and show those goods, which generate the greatest customer interest. Due to this, the products do not lie around unsold and the sales grow.
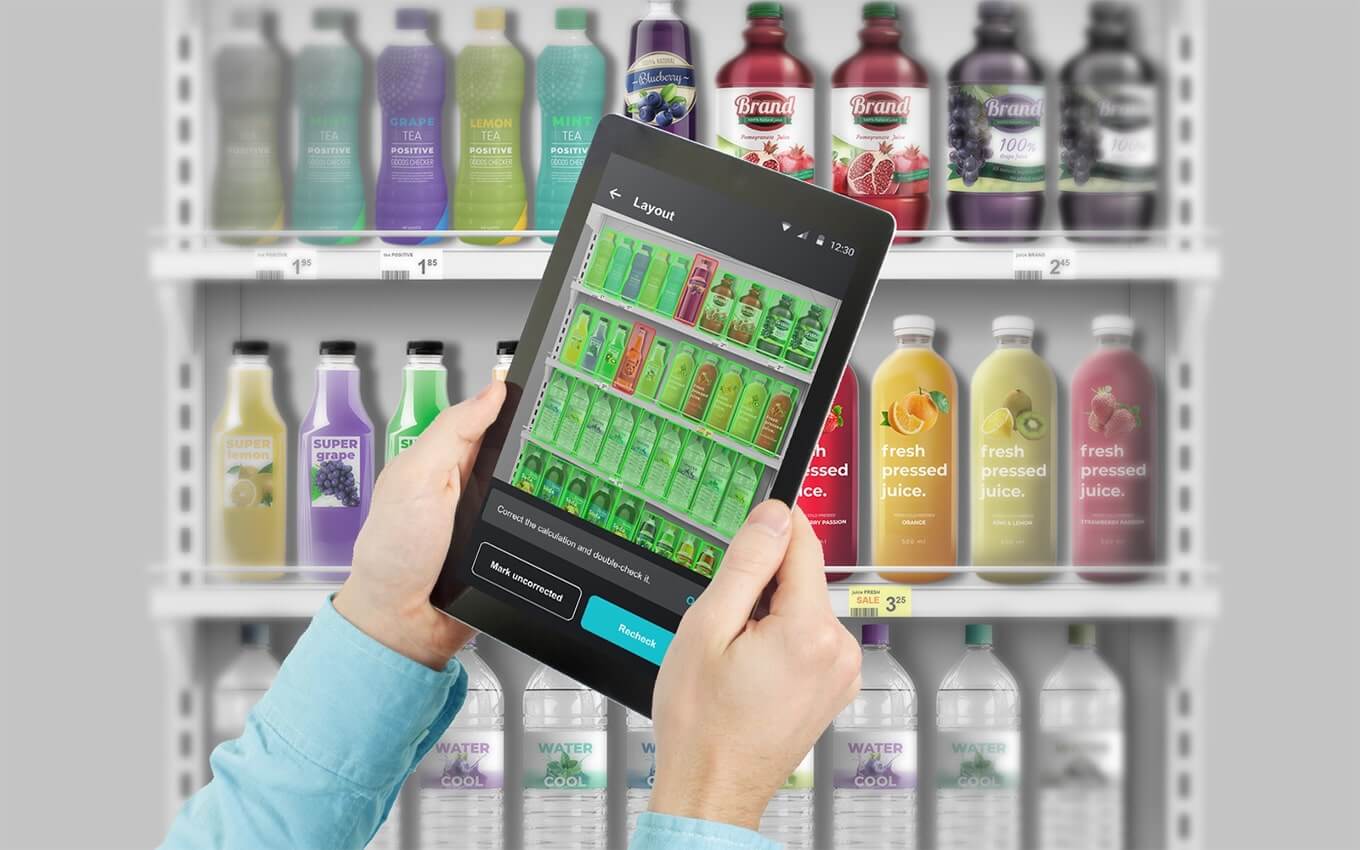
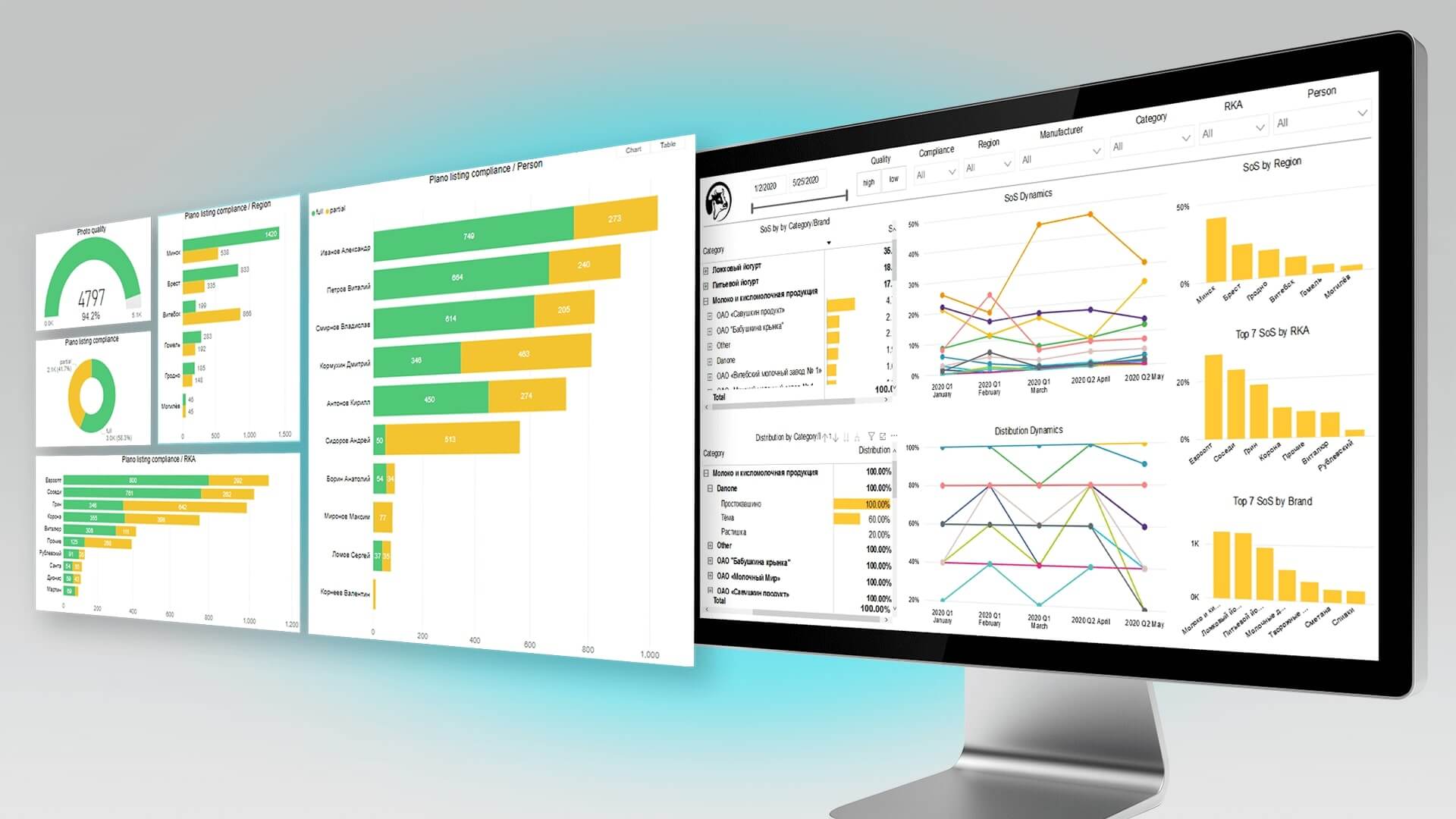
AI also collects analytical data. In this way, a company obtains the required information about the performance of the outlet, and is able to monitor the key indicators and improve processes. For instance, the company can monitor the number of SKUs, POS materials and prices, brand/SKU share on the shelves, any changes as compared to previous periods, any goods missing on the shelves, photo quality analytics, etc.
Many FMCG manufacturers and distributors in various regions have already launched pilot projects in the sphere of artificial intelligence and computer vision. For example, a European video surveillance systems integrator is offering computerised merchandise display monitoring for cafes and stores selling own ready-cooked foods, because employees were not able to serve customers and replenish goods on the shelves at the same time.
Goods Checker, a cloud-based solution, has been chosen to solve the problem. It uses computer vision to find empty spaces on the shelves. If a product is missing, the system instantly sends a message to the employees in charge via messenger.
Using computer vision solutions, retail traders and cafes have been able to identify peak demand periods and increase the products availability. Moreover, these solutions will help to increase sales due to constant monitoring of the availability of goods on the shelves and reduce the quantity of spoiled products due to accurate production planning.
Three Scenarios for AI Integration


Mobile app
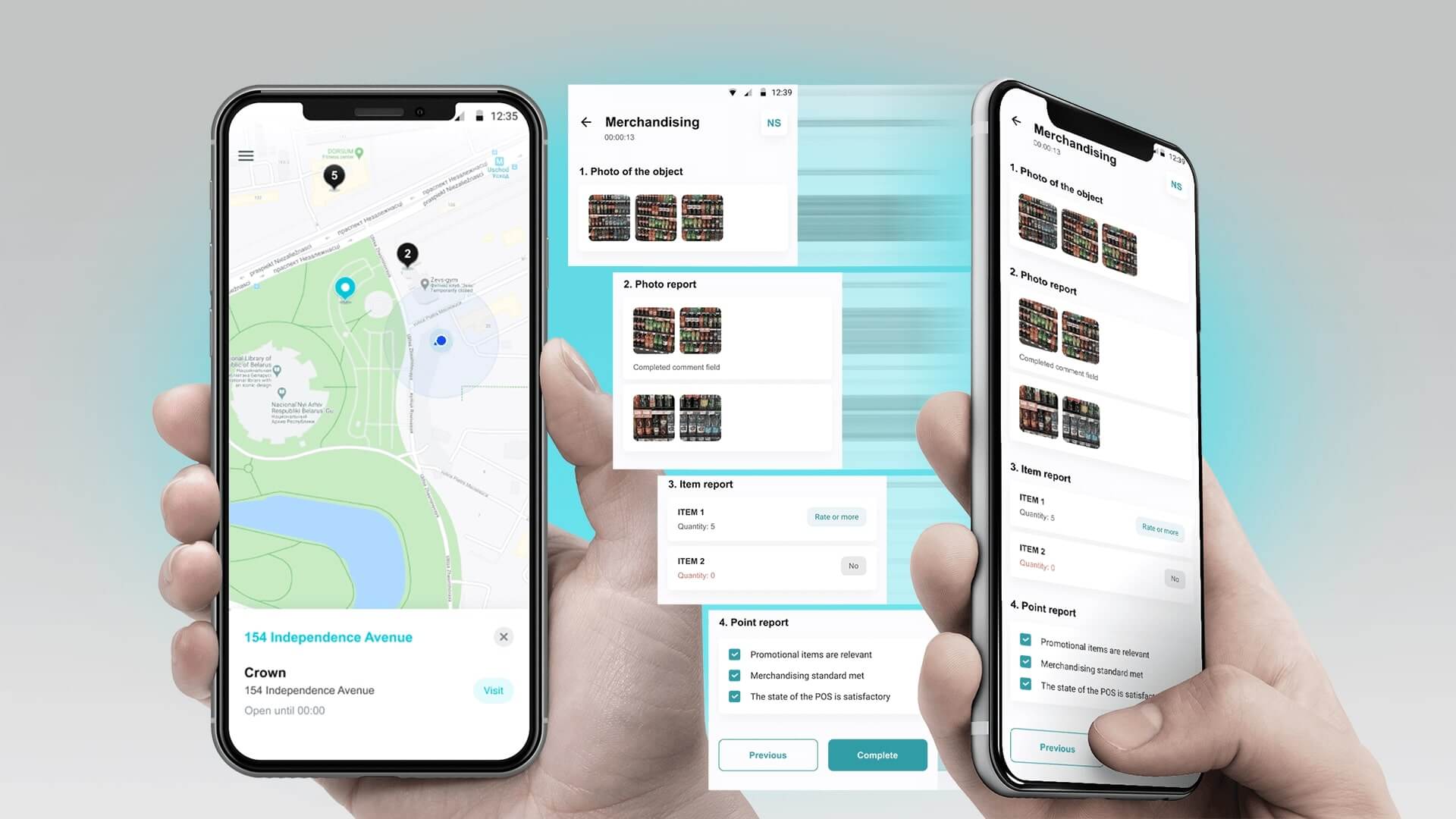
Using a mobile app with computer vision is an easy way to automate merchandising. The customer starts to use a ready-made application provided by the developer. The IT company can customise the app to suit specific needs of a particular business, if necessary. For example, it can add new indicators to be monitored, improve analytic features, etc.
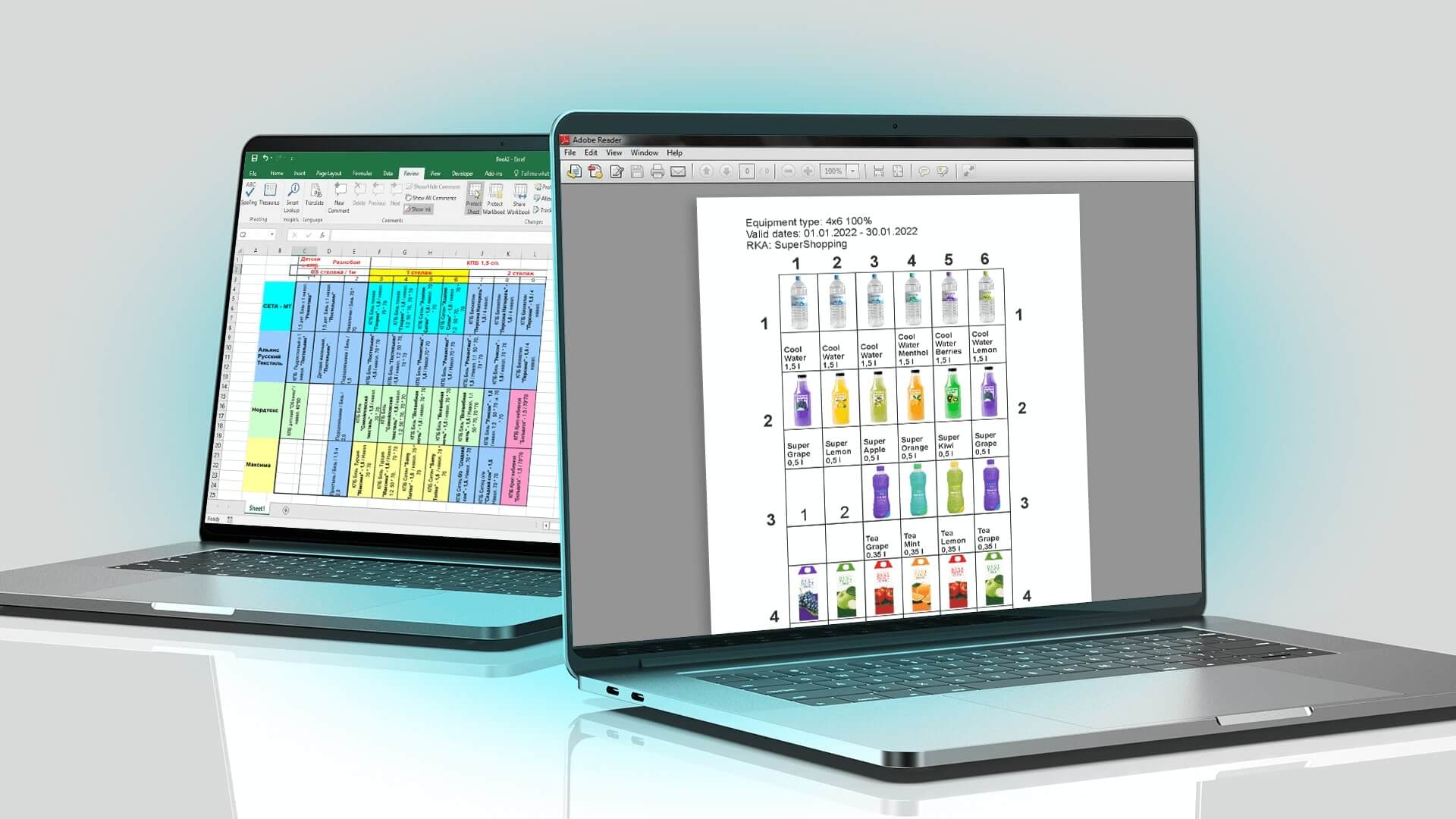
AI implementation simplifies monitoring of product availability on the shelves: employees just take photos of the shelves in the application and immediately see the results of the processing. The system shows whether the product display corresponds to the planogram. The ability to use the app without a permanent Internet connection is an important advantage, which is crucial in outlets where connection may be poor. The app generates reports that help managers to see performance of each employee and identify problem areas in different stores. Although this solution may be more costly as compared to other scenarios and may take several months to implement, the company finally gets its own tool customised to its specific needs.

Integration via API
Integration via API may be used by companies that already have their own corporate app. In this case, computer vision is simply embedded into an existing system. Employees still use the familiar apps, and the company saves money without the need to develop a new one.
This scenario allows flexible customisation of functions to suit the needs of a specific business – one can add new analytic indicators or change the existing ones in order to be used with the specific product groups. The implementation is quick and easy for personnel, since the main interface remains familiar to all participants in the process.

Integration via FTP server
FTP integration will be suitable for companies, which have to launch a project and test how the solution works within short timeframes. This method also may be used efficiently by businesses that do not require real-time analytics. A computer vision system is directly connected to the company’s existing server and automatically processes all photos uploaded to it. Employees may just follow the usual work process and they do not have to adapt to using new programs. This solution maybe implemented on tight schedule, which is critical for large retail chains with large volumes of accumulated information and a unified reporting system.Artificial Intelligence is a Crucial Factor for Success in Modern Retail Trade

The AI market is rapidly developing, creating significant advantages for FMCG manufacturers and distributors. State-of-the-art technologies allow automation of the key processes: from product placement monitoring to customer behaviour analysis. Due to various integration scenarios, even medium-sized businesses are able to implement such solutions with minimal changes in day-to-day operations.
A successful example of the video surveillance integrator clearly shows how computer vision is already helping businesses. Computerised monitoring of products availability on the shelves ensures expeditious response to demand fluctuations and provides management with key information required to make strategic decisions. Companies that already use these technologies have a significant advantage on the market, so you better be quick with the implementation of digital solutions.