In 2025, companies will face new challenges due to people’s increasing demands for a quality shopping experience, and their interest in digital innovation. So businesses will have to accommodate change.
According to statistics, the AI market in fast-moving consumer goods and retail is growing by almost 9% annually and will reach $1.565 trillion by 2033. This is just one example of how rapidly the fast-moving consumer goods industry is developing.
FMCG market is developing rapidly, and therefore especially requires consideration of the trends that will shape the industry in the near future. In this article we will tell you about key trends that FMCG company leaders need to pay attention to.
Key Takeaways:
- In-store analytics is transforming retail. Computer vision and machine learning systems in stores provide instant insights about shelf conditions and customer behavior. Goods Checker improves planogram compliance from 60% to 90%, reducing merchandising costs.
- Products for emotional health and longevity are gaining popularity. Despite rising anxiety, 52% of consumers believe they’ll be healthier in 5 years. Major brands are launching stress-relief teas (Lipton), sleep drinks (PepsiCo), and functional products with probiotics.
- Consumers are becoming more conscious. Impulse purchases dropped to 18%, while 57% of consumers thoroughly research products before buying. This creates demand for curated product selections and personalized recommendations instead of independent searching through overwhelming choices.
- Omnichannel unites online and offline. Companies are developing direct sales through their own channels: P&G launched online stores, Nike created an ecosystem for app ordering with in-store fitting and product personalization.
- Traditional retail models no longer work. Static pricing, simple apps without AI, and conventional stores are losing to brands with dynamic pricing, personalized recommendations, and eco-friendly solutions.
Table of Сontents
New Trends for 2025
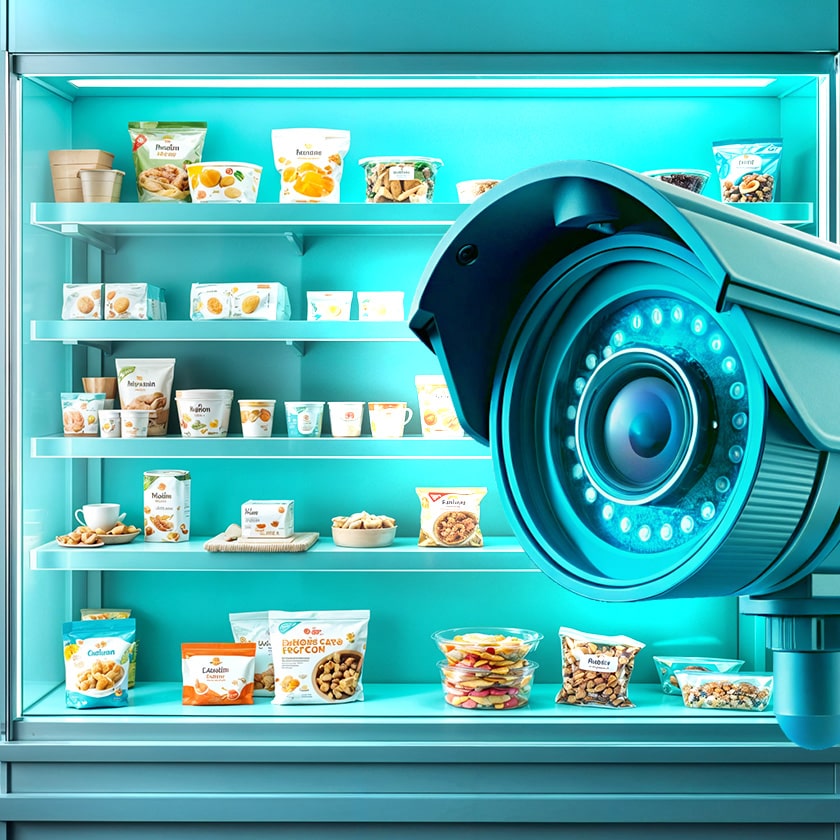

1. Smart Analytics Directly at Point of Sale
FMCG companies have actively begun implementing intelligent analytics solutions directly at points of sale. They use both cloud technologies (Cloud Computing) and local data processing (Edge Computing). Computer vision and machine learning systems help stores work faster and more efficiently, providing instant insights about store conditions and customer behavior.
Examples. AVS Services offers to its clients, both shops and cafes, to monitor availability of goods on display. To this end, the video surveillance cameras have an in-built computer vision system, Goods Checker, which automatically checks if there are any empty spaces on the shelves and notifies employees via messenger about the need to replenish goods. This way, Goods Checker helps to monitor availability of products on the shelves, and to check where the goods are scarce and which category of goods is missing.
A French retailer, Auchan, uses a similar system to ensure that shelves are always filled with goods.
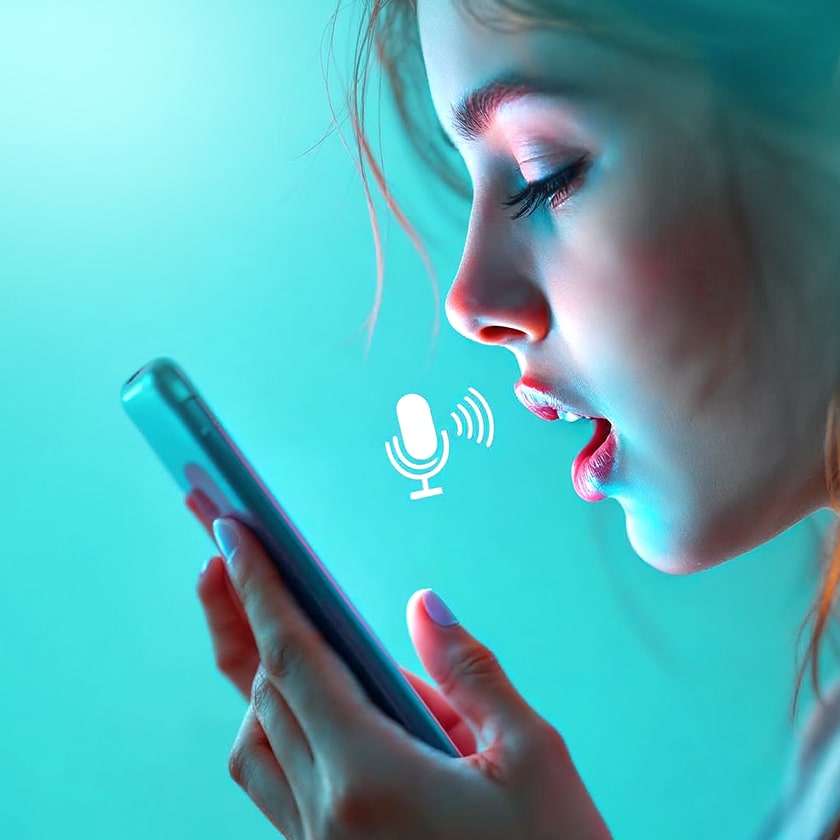

2. Generative AI and Voice Technologies
AI is changing the product creation process – from idea generation to packaging design. By analyzing data on consumer preferences and market trends, technology helps companies create products that precisely meet customer needs.
Generative AI effectively predicts demand by analyzing historical sales data, seasonal fluctuations, and economic factors. This allows companies to avoid both product shortages and excess inventory.
Voice technologies are becoming a new interface for ordering. Speech recognition systems that understand regional languages and dialects make shopping more convenient and accessible.
Examples. Nestlé uses a proprietary generative AI tool in its product innovation process that helps teams generate and test product ideas faster and more efficiently. The company applies AI to analyze information about trends, ingredients, flavors, and health benefits from social media and other web sources. P&G, in collaboration with Accenture, created an AI-based toolkit for developing consumer goods formulations.
PepsiCo created a voice AI system for B2B orders in Latin America that accepts orders through voice commands in local languages. The system uses automatic speech recognition and natural language understanding technologies, reducing order errors and speeding up the process by 40%.
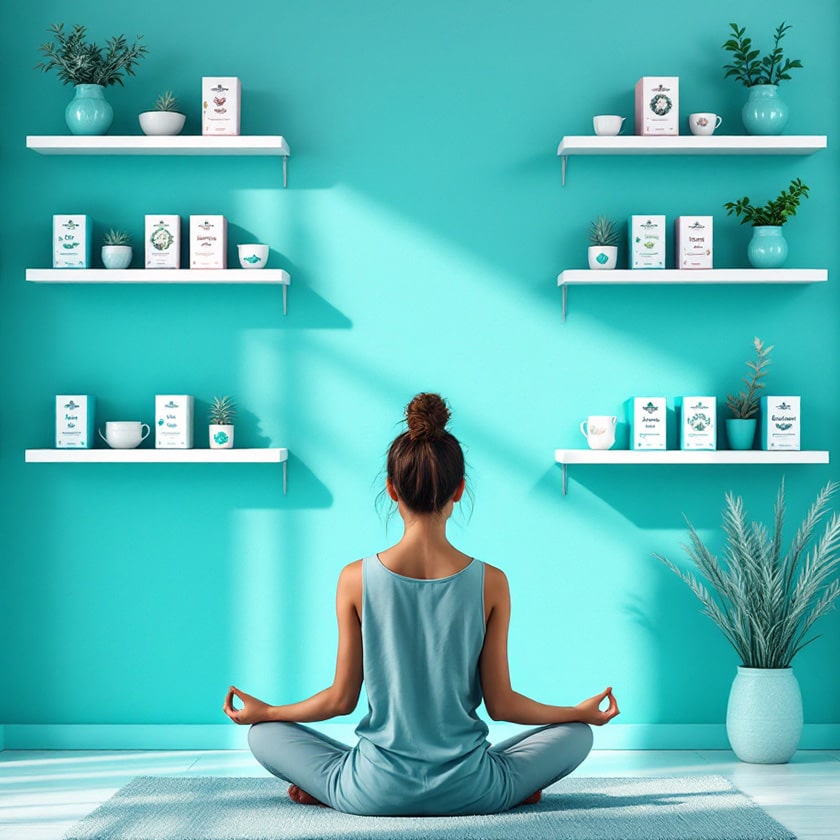

3. Products to Support Emotional and Mental Health
Products for emotional well-being are replacing ordinary products. Manufacturers respond to consumer demand by creating products that help manage stress, improve mood, and support overall quality of life. Despite the prevalence of anxiety and sleep problems, 52% of consumers believe they will be healthier in five years than they are now.
Alongside mental health care, the trend toward quality longevity is developing. It transforms the approach to health—instead of treating diseases, people focus on extending the period of active life. This creates demand for functional products with probiotics, antioxidants, and adaptogens. Companies develop specialized categories: energy support products for people over 50, memory-improving drinks, healthy weight maintenance snacks. Manufacturers consider the growing interest in preventive nutrition—products are positioned as tools for maintaining optimal body condition for years to come.
Example. Major food manufacturers have launched new product lines to support emotional health. Lipton from Unilever created the “Mood Therapy” tea series with calming herbs, PepsiCo developed Driftwell drinks to help relax and sleep better, and Nestle launched chocolate production with adaptogens for stress reduction.
Danone develops a line of yogurts with probiotics specifically designed to support gut health at different ages, while Unilever invests in research to create functional ice cream with added collagen and vitamins to maintain skin youth.
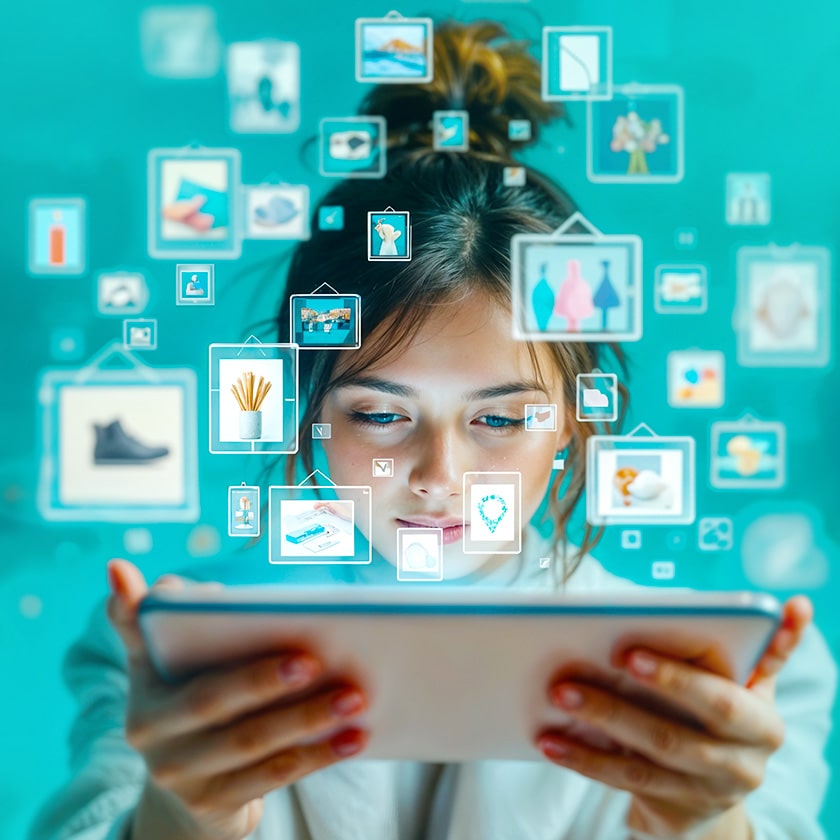

4. Conscious Consumption and Personalization
Consumers plan to save more and make fewer impulse purchases — for example, last year only 18% bought something spontaneously. Simultaneously, people are tired of information overload and huge choice, so they want to find needed products faster. This creates demand for ready-made product selections, personal recommendations, and AI assistants for choosing the right product.
Consumers have become more conscious: they carefully plan expenses, seek maximum value, and choose quality products. Statistics confirm this — 57% of respondents in 2024 studied products in detail before purchasing.
Examples. Amazon makes active use of machine learning algorithms to provide personalized recommendations. They analyze purchase history, product views and other data to offer users items that will be of interest to them.
Coca-Cola launched the “Share a Coke” campaign, where consumers’ names were printed on soda bottles. This created a personalization effect, allowing people to share drinks with their friends’ names or choose bottles with their own names.

5. Customer Experience: Engagement through Virtual and Augmented Reality
Technologies are increasingly used by companies in the FMCG industry. Innovation helps offer consumers not products alone, but also experiences. People love to play; they love interactivity, so companies are starting to make use of this in product promotion. For example, augmented and virtual reality creates more engaging and interactive product experiences. Buyers get involved, become interested and loyal to the brand, as they experience positive emotions. This trend makes brands more visible and improves consumer experience.
Examples. IKEA is using virtual reality technology to create virtual tours of its stores. Shoppers can “walk” through the store, view products and even place furniture in virtual interiors of their home to see how they would look.
L’Oreal has implemented AR technology to help customers choose cosmetics. Using the mobile app, customers can try on different shades of makeup or hair colors in real time using their device’s camera. This helps consumers see how the product will look on them before purchasing.
Still Trending since 2023

6. Comprehensive Digitalization: Innovations and AI-Powered Solutions in FMCG
Digitalization and innovation in artificial intelligence are changing processes in FMCG. They help improve production efficiency and streamline supply chains. This means that companies become more flexible and responsive to market changes.
CRM systems and automated support chats are the basis of any successful company. Now the trend is toward deeper and more complex automation, which affects not only manufacturers and distributors of FMCG/CPG goods, but also extends to consumers.
Deploying various tools and focusing on automation will allow improving customer satisfaction and creating a positive brand image. The main goal of automation is to optimize and improve the customer experience. Artificial intelligence solutions such as machine learning (ML) or computer vision (CV) help improve customer experience, enhance customer satisfaction, and thereby increase customer retention.
Example. With Goods Checker it is easier to manage the display and track out-of-stock situations. This automation will help present the product to the buyer the way you intended and ensure the availability of goods on the shelves. Thanks to the Goods Checker product, Alfa Distribution was able to effectively manage the presentation of goods on store shelves and reduce merchandising costs, which improved planogram compliance from 60% to 90% and significantly reduced the time of field audits.
7. Omnichannel and Direct Sales
FMCG companies are transitioning to an omnichannel approach, combining online and offline channels to create a seamless shopping experience. Consumers want to freely switch between digital and physical touchpoints—study products in apps, order online with store delivery, or buy in retail locations after online consultation.
Direct sales are becoming a key brand strategy. Companies develop their own D2C (Direct-to-Consumer) channels to control the entire customer journey—from product introduction to after-sales service. This allows collecting consumer data, personalizing offers, and building long-term customer relationships, bypassing intermediaries.
Examples. Procter & Gamble launched its own online stores for direct sales, allowing the company to better understand customer needs and offer personalized solutions. Nike develops an ecosystem where customers can order sneakers in the app, try them on in-store, and receive individual product customization.

8. Influencer Marketing on Social Media
Digital marketing growth remains an integral factor for FMCG business. Traditional TV and Google advertising continues losing effectiveness, requiring new channels.
For example, customers subscribe to bloggers and influencers on various social platforms like TikTok, Instagram, YouTube, etc.
Collaborating with social media influencers becomes an effective promotion method. Bloggers create trusting connections with audiences and influence purchasing behavior. FMCG companies use this, striving to improve product attractiveness for the young, digital generation.
Examples. Coca-Cola launched the #ShareTheMagic campaign on TikTok with content creators like Jalaiah Harmon and Khalid, which garnered over 11.9 billion views and increased TikTok followers by 71%.
Starbucks collaborated with K-pop group BLACKPINK, creating a souvenir product collection-items sold out online in the first 10 minutes, with long queues forming at physical stores before opening.

9. Big Data and Analytics
The use of big data and analytics is becoming part of the FMCG marketing strategy. Companies analyze customer data to better understand their preferences, behavior and needs. This ensures that marketing campaigns are finely tuned, products are modified according to customer requirements, and much more. All this helps the company better adapt to changes in the market.
Example. Coca-Cola, together with agency EssenceMediacom, launched a campaign based on retail data, targeting FairPrice customers who had purchased Coca-Cola products within the last 1-3 months — sales conversion data flowed to the platform daily, allowing the team to track campaign effectiveness in real-time.

10. Sustainable Development and Integrating Environmental Practices into Business Strategies
Sustainability is becoming not just the norm, but also a key growth driver for companies. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious and FMCG companies are actively implementing environmentally friendly practices. Avoiding single-use packaging, using recycled materials and energy-saving technologies are considered best industry practices. Companies that focus on these aspects not only strengthen and develop their brands in the market, but also attract the attention of environmentally conscious consumers. Example. Nestlé is committed to reducing its greenhouse gas emissions to zero by 2050. Moreover, the company has committed to making all its product packaging recyclable or reusable by 2025.Fading Trends

1. Conventional Retail Formats
Conventional retail formats are losing their attractiveness due to the development of digitalization and e-commerce. Consumers prefer convenience and brick-and-mortar stores are fading.
2. Statistical pricing models
Old approaches to pricing when prices change once a month based on a pre-approved plan do not apply any longer. The market requires flexibility: prices must adapt in response to demand, competitors’ actions and even depending on the time of day. Major retailers are already switching to smart pricing systems that automatically adjust prices to maximize profits.

3. Mobile apps without AI
Simple applications, which can be used just to browse through the catalog, accumulate loyalty points, and make purchases, do not meet the customers’ requirements any longer. Today, people want personalized recommendations, customized offers, and a convenient search. Therefore, the retailers actively build AI into applications to make them more adaptable to the needs of each customer.
4. Non-eco-friendly
As consumers become more environmentally aware, products and technologies that are not eco-friendly become less attractive. Ignoring environmental requirements is at risk of losing market share as consumers choose products that care about nature and sustainability.
5. Mass Unification
With the growing demand for uniqueness of products, mass unification is losing its attractiveness. Consumers desire individuality, which threatens the mass production of standardized products.
6. Premium Products
The trend towards increasing the premium quality of products is becoming less relevant as consumers value affordability and functionality. Brands that have strived for a premium positioning are forced to rethink their strategies and focus on quality and affordability.Following Trends is an Opportunity to Win over Consumers and Drive up Profits

FMCG industry in 2025 faces new challenges. Companies are adapting to trends and offering products that respond to consumer needs and participate in creating a sustainable future. The digital age presents opportunities, and brands that incorporate these trends into their strategy will be positioned to lead the way.
FAQ
- Immediate store-level analytics with edge computing. Retail outlets now perform real-time processing of shelf data on-site, even offline. Computer vision built into cameras can flag empty shelves and notify staff right away.
- Generative AI and voice technologies. Generative AI is used for product creation, packaging design, and demand forecasting by analyzing consumer data and market trends. Voice technologies with speech recognition make ordering more accessible, supporting regional languages and speeding up B2B and B2C processes.
- Product innovation for emotional and mental health. Brands like Lipton Mood Therapy, PepsiCo Driftwell, and adaptogen chocolate from Nestlé target stress relief and well-being.
- Immersive customer engagement using AR and VR. Companies like IKEA and L’Oréal deploy AR and VR experiences allowing consumers to virtually test products like furniture and cosmetics in real time.
- Direct-to-consumer (D2C) channel acceleration. FMCG brands increasingly engage customers directly via their own online platforms, reducing retailer dependence and enabling personalized offers.